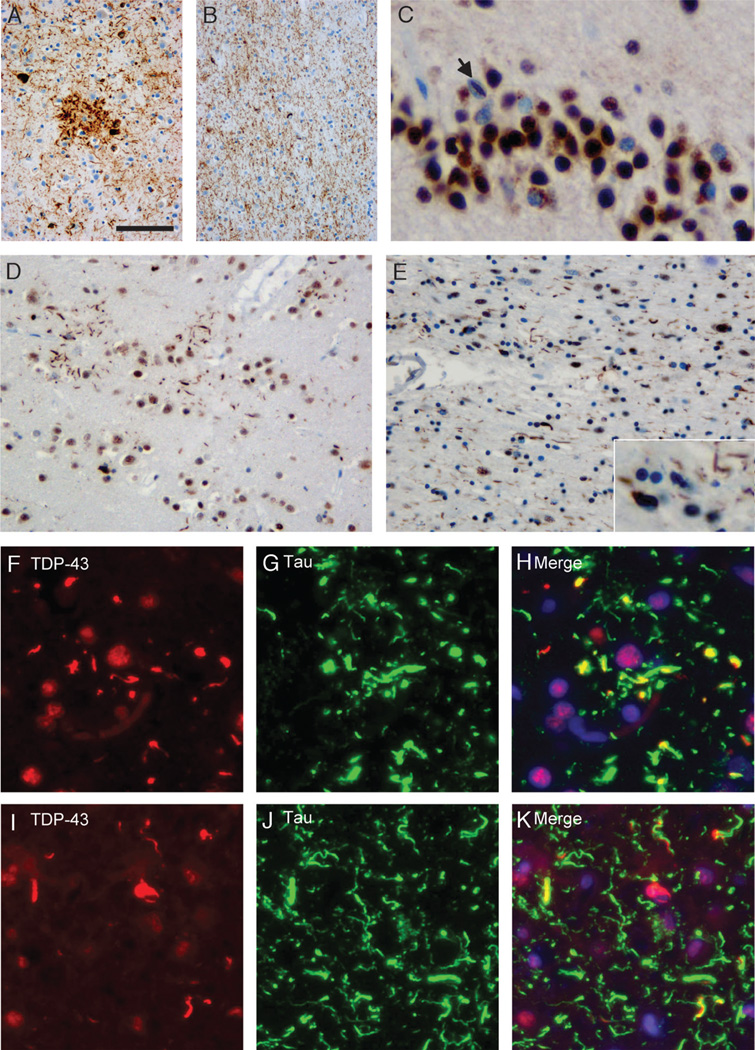
FIGURE 2.
Pattern of tau and TAR-DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) pathology in CBD. Anti-tau immunohistochemistry reveals characteristic features of corticobasal degeneration with astrocytic plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and numerous dystrophic neurites in the frontal gray matter (A) and numerous threadlike processes and coiled bodies in the white matter (B). (C) Immunohistochemistry of the same case with anti-TDP-43 showed neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions in dentate granule cells with a single neuronal intranuclear inclusion (C; arrow). In the frontal gray matter, there are several TDP-43-positive threadlike inclusions that are often arranged in annular clusters resembling astrocytic plaques (D). The frontal white matter shows TDP-43-positive threadlike processes and oligodendroglial inclusions (E). Double label immunofluorescence for TDP-43 (F, I) and tau (G, J) with merged images (H, K) shows partial colocalization of most TDP-43-positive threadlike inclusions with tau in the frontal gray matter. A small subset of inclusions is labeled by TDP-43 alone, whereas numerous tau-inclusions are TDP-43 negative (F–H). In the frontal white matter, TDP-43-positive threadlike inclusions partially colocalize with tau. In addition, there are inclusions that are single labeled for either tau or TDP-43 (I–K). Scale bars = (A) 100 (A, B); 50 (D, E); 25 (C; insert in E); 20 (I–K); and 15 µm (F–H).