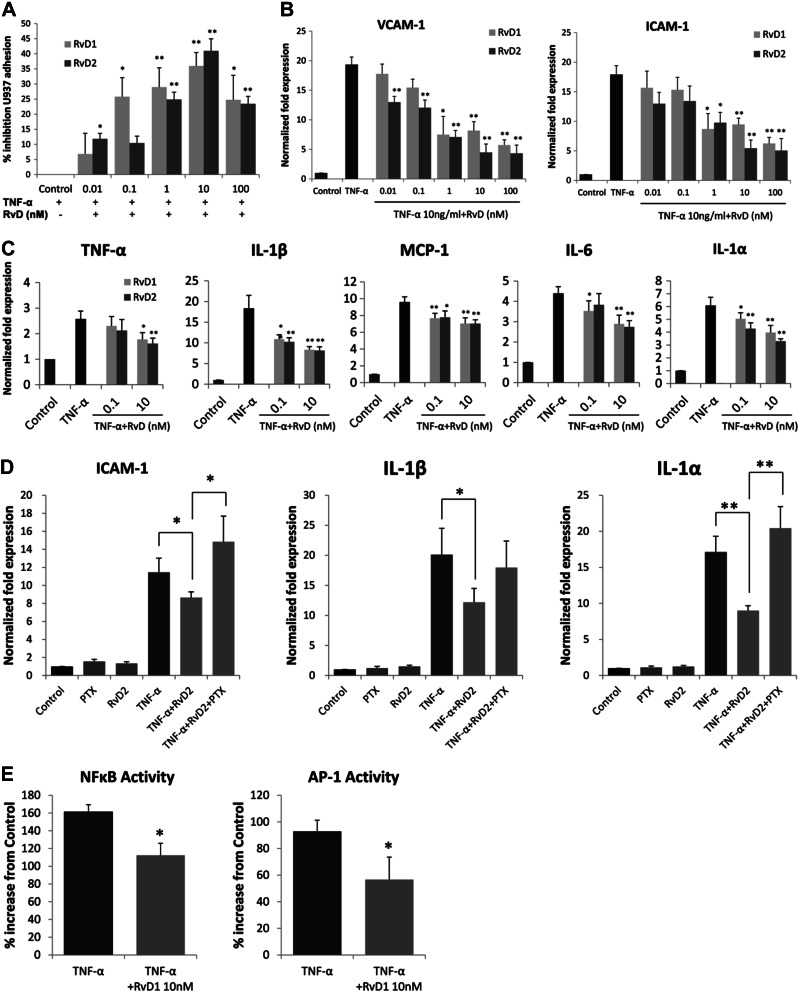
Figure 2.
Modulation of VSMC inflammatory responses by RvD1 and RvD2. A) Monocyte adhesion to VSMCs. HVSMCs were stimulated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 4 h, in the presence or absence of RvD1 or RvD2 at the indicated doses. Labeled U937 monocytes were overlain, and cell adhesion assay was performed as described. Results are shown as relative percentage inhibition, expressed as a percentage of the maximal adhesion for the agonist (n=3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; unpaired t test. B) RvD1 and RvD2 reduce cell adhesion molecule gene expression in VSMCs. VSMCs were treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 18 h in the presence or absence of RvD1 or RvD2 across a concentration range as shown. Expression of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 was measured by quantitative RT-PCR (n=3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; unpaired t test. C) Proinflammatory gene expression. VSMCs were stimulated with TNF-α as above in the presence or absence of RvD1 or RvD2 (0.1 nM or 10 nM), and qPCR was performed for multiple proinflammatory gene transcripts. Shown are significant reductions in the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, MCP-1, IL-6, and IL-1α (n=3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; unpaired t test. D) Effects of RvD2 on TNF-α stimulated gene expression in VSMCs are sensitive to PTX. VSMCs were exposed to TNF-α and RvD2 (10 nM) as described, in the presence or absence of PTX (100 ng/ml). RNA was harvested and analyzed for the expression of ICAM-1, IL-1β, and IL-1α by qPCR (n=3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test). E) RvD1 modulates activity of transcription factors NFκB and AP-1 in TNF-α-stimulated VSMCs. VSMCs were treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) with or without RvD1 (10nM for 2 h), and nuclear extracts were prepared. Transcription factor activity was assessed as described in Materials and Methods (n=5). *P < 0.05; unpaired t test. Results are means ± se.