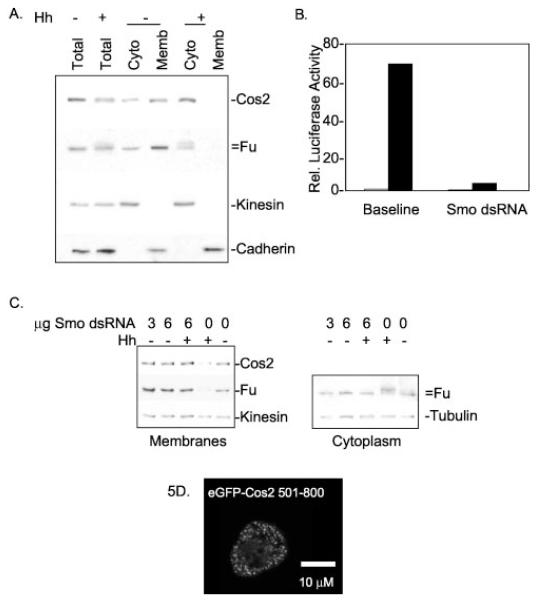
Fig. 5. The HSC association with membranes is Hh-sensitive and independent of Smo.
A, S2 cells were transfected with Hh or a control vector. Two days post-transfection, cells were lysed in hypotonic lysis buffer and fractionated as described under “Experimental Procedures.” 0.5× total lysate, 1× postnuclear cytosol (Cyto), and 1× total membrane (Memb) samples were normalized to volume, separated by SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted. Kinesin and Cadherin serve as positive controls for soluble and membrane-associated proteins, respectively. Kinesin is generally about 70% soluble upon hypotonic lysis, while the remainder associates with vesicles (61, 63). Cos2 and Fu are more cytoplasmic in Hh-treated cells. B, Cl8 cells were transfected with a ptc-Luciferase reporter construct and treated with or without dsRNA homologous to Smo in the presence or absence of Hh. Relative luciferase activity was measured post-lysis and demonstrates reduced Hh-activated transcription in cells treated with Smo dsRNA. White bars indicate −Hh; black bars indicate +Hh. C, S2 cells were transfected with Hh or a control vector with or without the addition of Smo dsRNA. Two days post-transfection, cells were hypotonically lysed and fractionated into postnuclear cytosol and total cellular membranes. Left panel, total cellular membranes separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for Fu, Cos2, and Kinesin. Fu and Cos2 continue to fractionate with membranes despite Smo dsRNA treatment. Right panel, postnuclear cytosols are immunoblotted for Fu and Tubulin. This panel demonstrates that the Hh-induced phosphorylation of Fu does not occur in cells treated with Smo dsRNA, verifying depletion of Smo in these cells. D, S2 cells were transfected with eGFP-Cos2-(501–800), which expresses a fusion protein that contains the membrane binding domain of Cos2 but not the Smo association domain. Confocal microscopy reveals that eGFP-Cos2-(501–800) distribution is similar to full-length Cos2; eGFP-Cos2-(501–800) is both cytoplasmic and punctate. Thus Cos2 does not require a Smo association domain to tether eGFP to vesicles. Rel., relative.