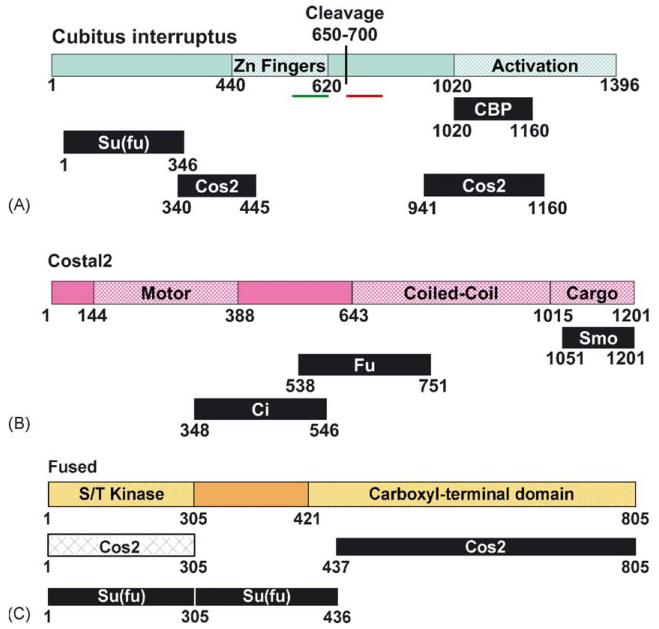
Fig. 2.
Functional domains of Hh signaling components. Indicated are the consensus interaction domains for each of the trimeric HSC components. Additional low affinity interactions that are not indicated may exist, and be involved in maintenance of HSC integrity. (A) Cubitus interruptus (Ci). Schematic of the transcription factor Ci, diagramming the Zinc finger domain [54], putative cleavage site [32] and activation domain. The putative nuclear localization sequence (amino acids 581–616 [96]) is indicated in by a green bar. The putative nuclear export sequence (amino acids 675–860 [97]) is indicated by the red bar. Interaction domains for binding partners CBP [70], Su(fu) and Cos2 [83,84] are also indicated. (B) Costal2 (Cos2). Schematic of the KRP Cos2, diagramming the motor domain, coiled-coil and cargo domains. Also indicated are interaction domains for Hh pathway binding partners Smo [75,76,94,95], Fu and Ci [83,84]. (C) Fused (Fu). Schematic of the serine/threonine protein kinase Fu, diagramming the kinase and carboxyl-terminal functional domains [82]. Also indicated are interaction domains for Hh pathway binding partners Cos2 and Su(fu) [83-85].