Fig. 3.
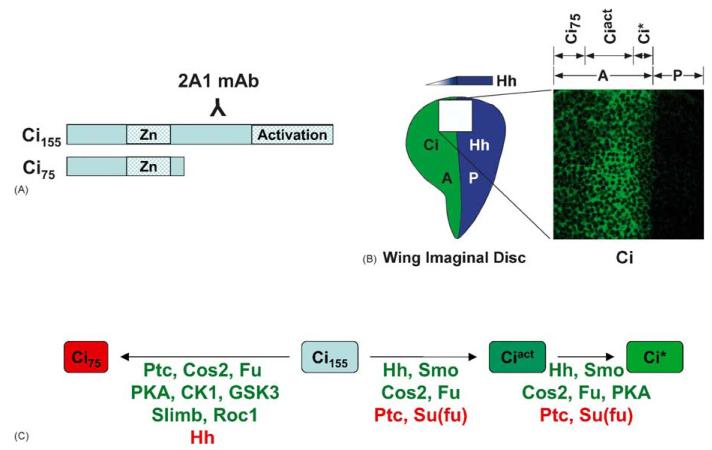
Hedgehog sensitive processing of Cubitus interruptus. (A) Schematic of Ci155 and Ci75 depicting the epitope of the 2A1 monoclonal antibody. (B) The Ci gradient in the Drosophila wing imaginal disc. Late third instar wing imaginal discs were immuno-stained with 2A1 monoclonal antibody. Hedgehog diffuses from the Posterior (P) compartment to affect production of Ci activator species in Anterior (A) compartment cells. Cells near the A/P compartment boundary, receiving the highest level of Hh stimulation convert Ci155 to the enhanced transcriptional activator Ci*. It is evidenced by decreased detection of Ci by the 2A1 monoclonal antibody. Cells further into the A compartment accumulate Ciact, as evidenced by more intense Ci staining, which results from decreased Ci proteolysis. Cells far into the A compartment contain higher amounts of Ci75, which is not detected by the 2A1 antibody. (C) Hedgehog sensitive Ci processing is dependent on multiple Hedgehog signaling components. Factors listed in green promote conversion to the indicated Ci species. Factors listed in red prevent conversion.