Figure 1.
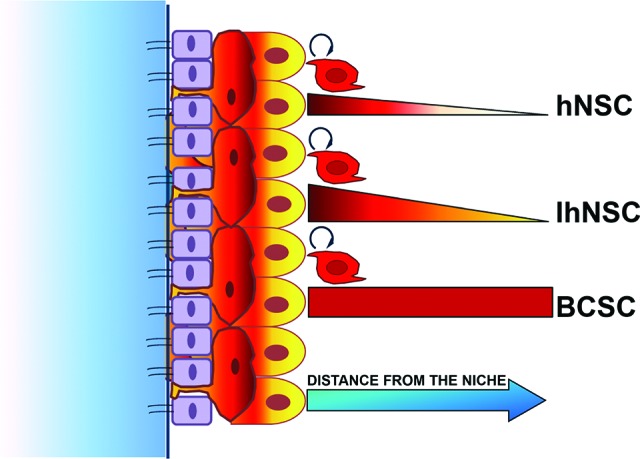
Model of the niche-dependent self-renewal capacity of neural stem cells and BCSCs. Untransformed cells, namely hNSCs or IhNSCs, which display a growth factor-dependent self-renewal in vitro, are able to self-renew in vivo only if implanted in proximity of a stem niche area, whereas BCSCs maintain a cell-autonomous self-renewal capacity both in vitro and in vivo. Red bars measure self-renewal capacity of hNSCs, IhNSCs, and cancer stem-like cells by two parameters: the kinetic and the long-term maintenance. In particular, red color gradations correlate with proliferation rate, which is higher in IhNSCs and BCSCs than in hNSC. The thickness of the red bars indicates the maintenance (for BCSCs) or the shortening (for hNSC and IhNSC) of self-renewal capacity, dependent on the distance from the niche. Abbreviations: BCSC, brain cancer stem cell; hNSC, human neural stem cell; IhNSC, immortalized human neural stem cell.
