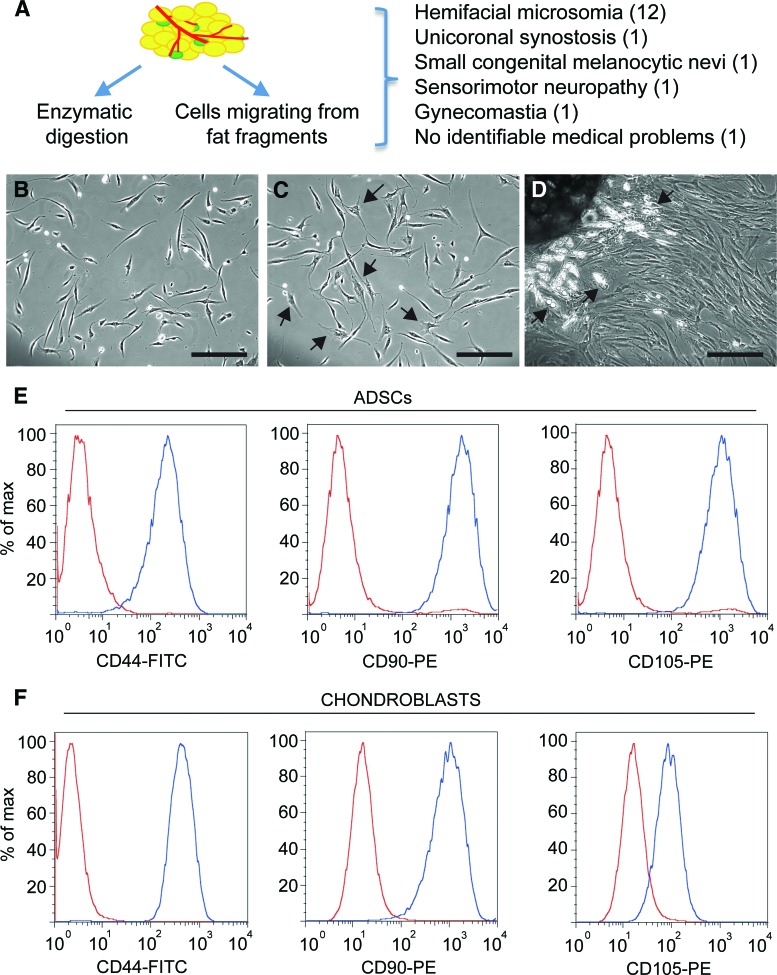
Figure 1.
Phase images of ADSC and adipose explant dedifferentiated stem cell cultures. (A): Diagram indicating the two approaches used to obtain adipose tissue-derived stem cells from pediatric abdominal fat and summary of donors' conditions (details can be found in supplemental online Table 1). (B): ADSC morphology at passage 1. (C): ADSC morphology at passage 4. Note the appearance of cells with a more spread out morphology and increased cytoplasm/nucleus ratio (arrows). (D): Adipose tissue explant from which cells are migrating. Cells have a multilocular morphology close to the explant (arrows) and become fibroblastic as they migrate away from it. (E, F): Expression of the cell surface proteins CD44, CD90, and CD105 assessed by flow cytometry in ADSCs (E) and chondroblasts (F) from the same patient (red curves: negative controls; blue curves: labeled cells). Scale bar = 200 μm. Abbreviations: ADSC, adipose-derived stem cell; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; max, maximum; PE, phycoerythrin.