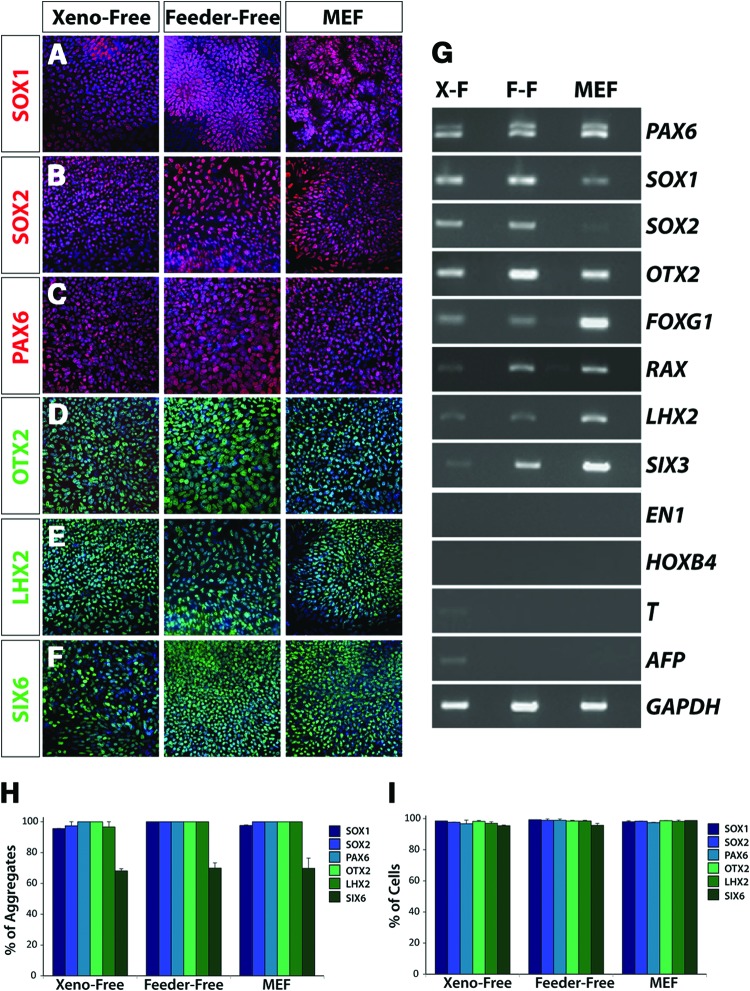
Figure 2.
Primitive retinal specification of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) grown under xeno-free conditions. Within the first 10 days of differentiation, hiPSCs acquired features of the primitive anterior neuroepithelium under all growth conditions. (A-C): The near uniform expression of SOX1, SOX2, and PAX6 indicated the acquisition of a primitive neural fate from hiPSCs. Magnification, ×20. (D–F): hiPSCs also expressed retinal-associated genes including OTX2, LHX2, and SIX6. Magnification, ×20. (G): Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis highlighted similar patterns of gene expression across all growth conditions at this time point. Importantly, in addition to the expression of early neuroretinal genes, the regional and temporal specificity of gene expression was confirmed through the absence of genes including EN-1, HOXB4, BRACHYURY, and AFP. (H, I): Quantification of immunocytochemistry experiments revealed comparable percentages of cell aggregates that expressed the indicated transcription factors (H), as well as equivalent percentages of cells within immunopositive aggregates expressing each transcription factor (I). Magnification, ×20. Abbreviations: F-F, feeder-free; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblast; X-F, xeno-free.