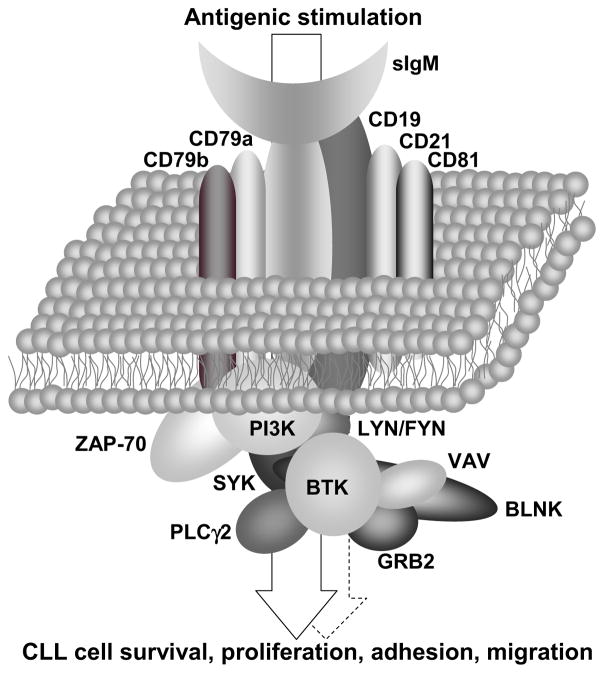
Figure 2.
The B-cell receptor – a signaling complex that delivers microenvironmental-derived information into the CLL cell. The sIgM serves as the backbone of the BCR, and is associated with other transmembrane molecules (e.g. CD19, CD21). The transmembrane components of the BCR associate with a variety of enzymes (e.g. SYK, BTK) and scaffold proteins (e.g. BLNK) to form a signaling complex. This complex translates extracellular cues, predominantly antigenic stimulation, into CLL cellular responses including survival, proliferation, adhesion and migration (arrow). Tonic or cell-autonomous activation (dashed arrow) does not require extracellular stimuli.