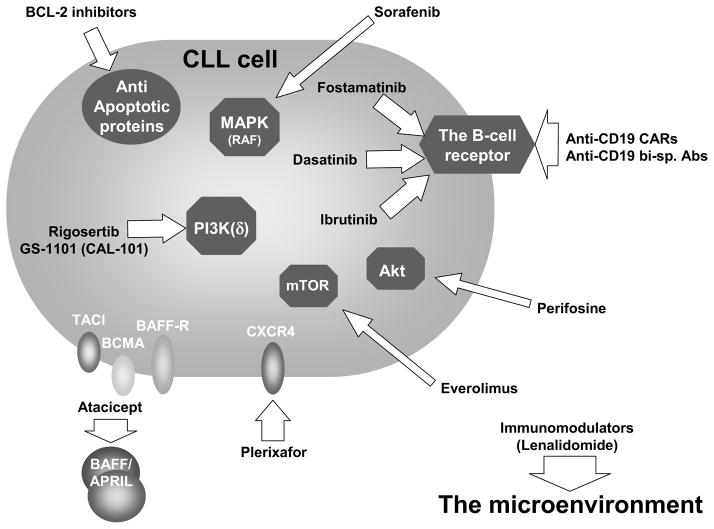
Figure 3.
Therapeutic targeting of microenvironmental-induced signaling in CLL. Current and experimental CLL therapeutics (arrows) target the various components of the microenvironment-CLL milieu and its associated signaling network. Thus the BCR and its associated components are targeted by antibodies (anti-CD19) or small molecules (e.g. SYK (e.g. fostamatinib) or BTK inhibitors (e.g. ibrutinib)). Small molecules are also utilized to inhibit mTOR, Akt, PI3K(δ) and the MAPK cascades. Extracellular inhibitors such as plerixafor or atacicept can block the association of SDF-1 or BAFF/APRIL, respectively, with their receptors on the CLL cell. Both the microenviroment (e.g. the immune system) and the outcome of its signaling responses in the CLL cells (e.g. upregulation of BCL-2) are avenues for therapeutic targeting.