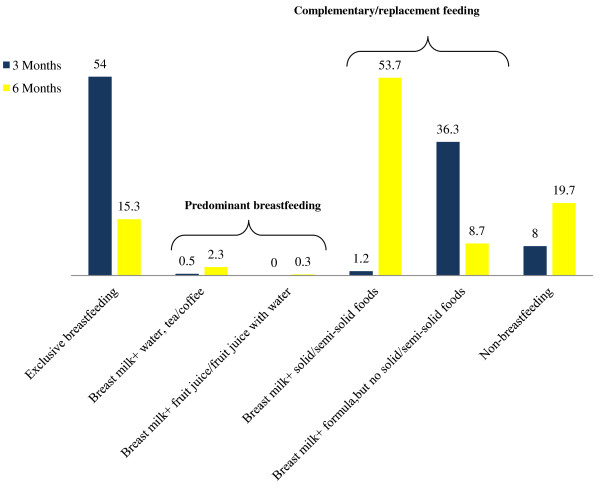
Figure 3.
Detailed breakdown of infant feeding categories during 3 and 6 months postpartum in a subsample of participants from the first phase of Alberta Pregnancy Outcomes and Nutrition (APrON) study1,2. (legend) 1Categories were defined based on the infant feeding guidelines of the World Health Organization. 2Non-breastfeeding: requires that infants receive no breast milk (directly, expressed, or from a wet nurse) and could be fed any solid/semi-solid foods or liquids including non-human milk. Complementary feeding/replacement feeding: requires that infants receive breast milk (directly, expressed, or from a wet nurse) and solid/semi-solid foods, food-based liquids, or non-human milk. Predominant breastfeeding: requires that infants receive breast milk (directly, expressed, or from a wet nurse) as the main source of nourishment and allows feeding of certain liquids (water, water-based drinks, and fruit juice), ritual drinks, ORS, drops, and syrups (vitamins, minerals, medicines). Infants in this category are not allowed to receive anything else especially non-human milk and food-based fluids. Exclusive breastfeeding: requires that infants receive breast milk (directly, expressed, or from a wet nurse) and only allows intake of drops and syrups (vitamins, minerals, medicines). Infants in this group are not allowed to receive anything else.