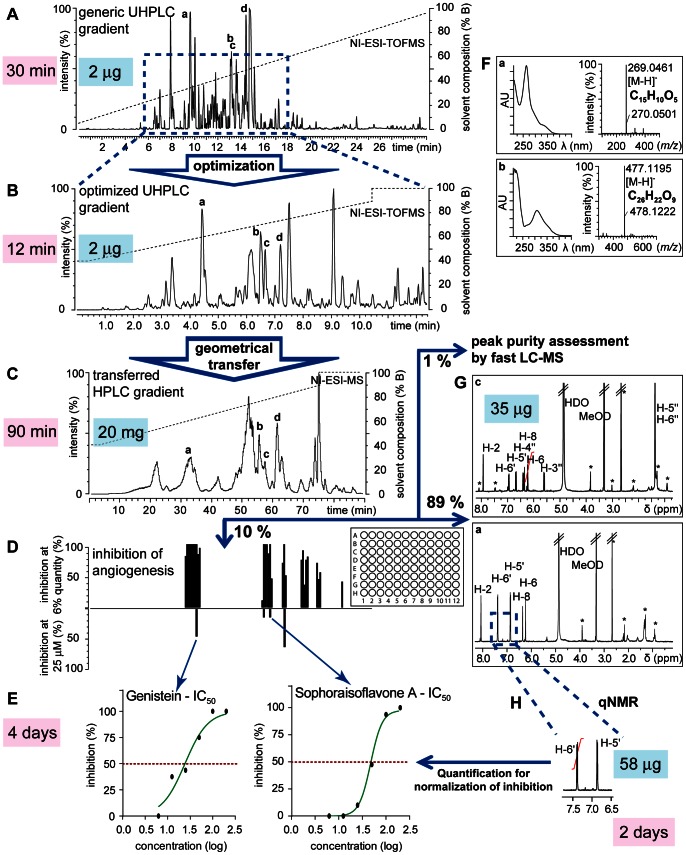
Figure 3. Generic procedure for the rapid identification of bioactive constituents from medium polar plant extracts.
A, Generic ultra high pressure liquid chromatography – photo diode array – time of flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-PDA-TOFMS) chromatogram. UHPLC conditions: Acquity BEH C18 column (150×2.1 mm i.d., 1.7 µm); A: 0.1 vol% formic acid (FA)-H2O, B: 0.1 vol% FA-acetonitrile, 5–95% B in 30′; 0.46 mL/min; ESI-MS detection in negative ion (NI) mode; B, Optimized UHPLC-PDA-TOFMS chromatogram for methanolic extract of R. viscosa. UHPLC conditions: Acquity BEH C18 column (100×2.1 i.d., 1.7 µm); A: 0.1 vol.% FA-H2O, B: 0.1 vol% FA-methanol (MeOH), 40–90% in 11.4′; 0.306 mL/min, ESI-MS detection in NI mode; C, Semi-preparative high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) chromatogram for the microfractionation of the enriched extract of R. viscosa. HPLC conditions: XBridge™ BEH C18 column (250×10 mm i.d., 5 µm); A: 0.1 vol.% FA-H2O, B: 0.1 vol% FA-MeOH, 40–90% in 74.9′; 2.3 mL/min; ESI-MS detection in NI mode. The chromatographic gradient is geometrically transferred using mathematical models to obtain a comparable elution of extract constituents. Fractions were collected every 30 s directly into 96-deepwell plates. The so generated microfractions were aliquoted for anti-angiogenic screening (10% aliquot A), for fast LC-MS analysis (1%, aliquot B), and for NMR analysis (89%, aliquot C); D, Anti-angiogenic screen on 180 microfractions generated by microfractionation. Positive bars show inhibition of angiogenesis of microfractions tested at high concentration; negative bars show inhibition of angiogenesis of selected microfractions at 25 µM. The concentration was determined by quantitative NMR (qNMR) (H); E, Determination of IC50 using the quantitative information obtained by qNMR (H); F, On-line PDA and high-resolution MS information from (A) for the dereplication of plant constituents; G, 1H NMR spectra using the CapNMR™ probe for structure confirmation of bioactive constituents; H, Integration of well resolved aromatic protons for quantification of bioactive constituents to establish the potency of the anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory activity of the targeted compounds (D, E).