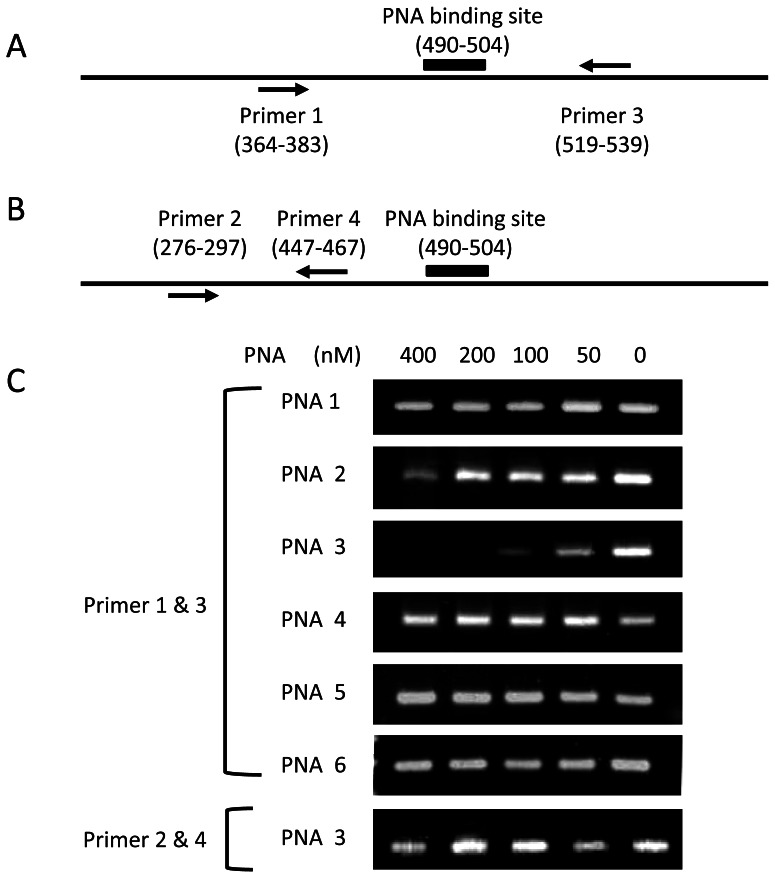
Figure 2. Inhibition of reverse transcription of the NS gene of influenza A/Osaka/180/2009(H1N1) virus by PNA 1–5.
A), B) Schematic diagram of the PNA binding site and the primer target sites on the nonstructural protein (NS) gene. Primers 1 and 3 were used to amplify duplex DNA coding nt 364–539 of the NS gene, which contains the PNA binding site. Primers 5 and 6 were used to amplify duplex DNA coding nt 276–297 that does not contain the PNA binding site. PNA 3 inhibited DNA amplification with the primers that amplified duplex DNA containing a PNA binding site on the NS gene. C) Agarose gel analysis of the virus gene transcripts in the presence of the indicated PNA. The NS gene was reverse transcribed into cDNA by Moloney murine leukemia virus (MuLV) reverse transcriptase and then amplified into dsDNA by PCR. The PCR products were analysed by gel electrophoresis on 2% agarose gels. Conditions: 0, 50, 100, 200 or 400 nM of PNAs and 6×104 pfu/ml virus solution were dissolved in 10 mM Na2HPO4 buffer (pH 6.9) containing 0.1% Triton X-100 solution. Incubation: 25°C for 30 min and then reverse transcribed into cDNA by MuLV reverse transcriptase. The cDNA solution was diluted 50-fold and amplified into dsDNA by a standard PCR reaction.