Figure 3. MARCKS inhibits acrosomal exocytosis and this effect is dependent on phosphorylation.
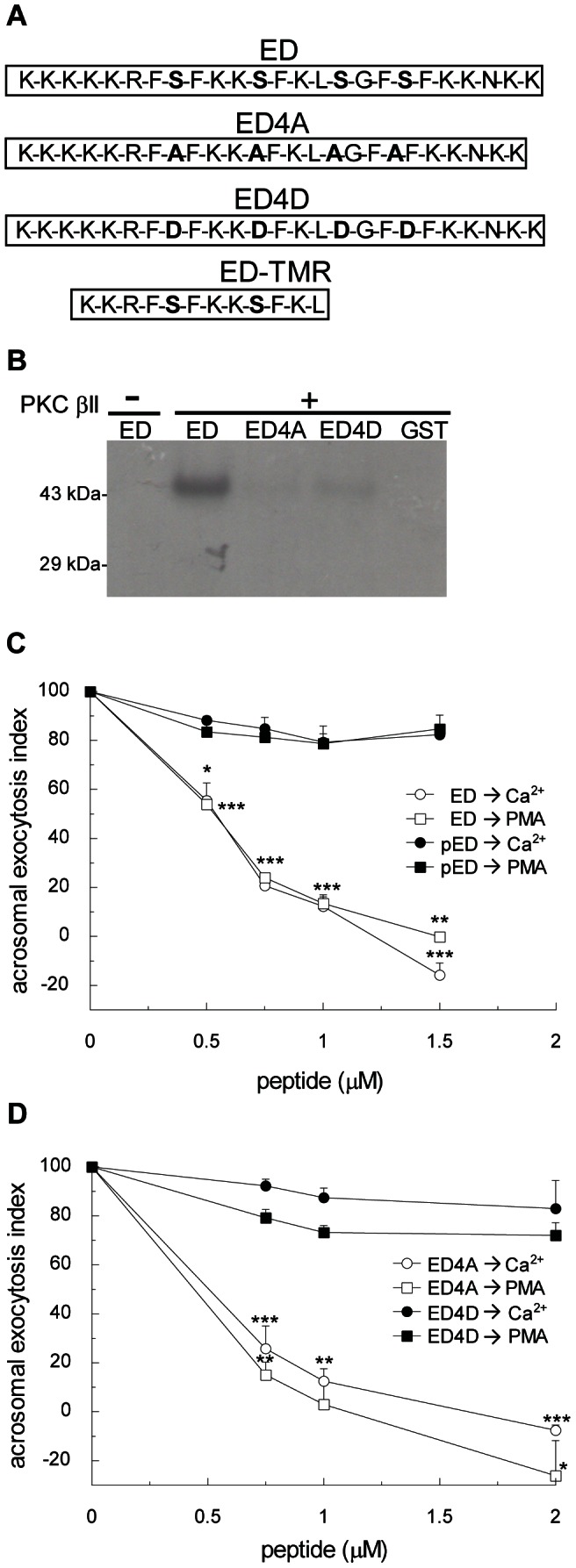
(A) Amino acid sequence (residues 145–169) of mouse wild type MARCKS effector domain (ED), the non-phosphorylable MARCKS ED mutant (ED4A), the phosphomimetic MARCKS ED mutant (ED4D), and permeable tetramethylrhodamine-conjugated MARCKS ED peptide (ED-TMR). (B) Purified GST fusion proteins of wild type MARCKS ED (ED), MARCKS ED4A mutant (ED4A), MARCKS ED4D (ED4D), and GST (26 kDa) were incubated for 40 minutes at 37°C with (+) or without (-) PKC βII under activating conditions in the presence of [γ32P]ATP. Samples were then resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE gels, and radiolabeled proteins were detected by autoradiography. Shown is a representative gel from three independent experiments. (C) Permeabilized sperm were treated for 15 minutes at 37°C with increasing concentrations of MARCKS effector domain (ED, white symbols) or in vitro phosphorylated MARCKS ED (pED, black symbols). Acrosomal exocytosis was initiated by adding 10 µM free Ca2+ (circles) or 200 nM PMA (squares). In all conditions, the incubation continued for an additional 15 minutes and acrosomal exocytosis was evaluated by lectin binding. (D) Permeabilized sperm were treated for 15 minutes at 37°C with increasing concentrations of MARCKS ED4A (ED4A, white symbols) or MARCKS ED4D (ED4D, black symbols). Acrosomal exocytosis was initiated by adding 10 µM free Ca2+ (circles) or 200 nM PMA (squares). In all conditions the incubation continued for an additional 15 minutes and acrosomal exocytosis was evaluated by lectin binding. In C and D, the percentage of reacted sperm was normalized as described in Materials and Methods. The data represent the means±SEM of at least three independent experiments. The asterisks indicate significant differences from similar conditions stimulated with Ca2+ (*, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001).
