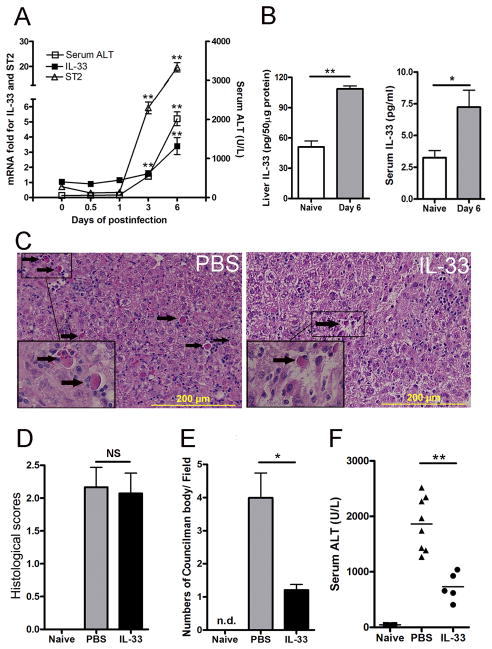
Figure 1. IL-33 was involved in viral hepatitis and attenuated liver damage.
B6 mice were i.v. injected with AdLacZ (3 × 109 PFU/mouse). A) Mice were sacrificed at the indicated time points. IL-33 and ST2 expression was analyzed by qRT-PCR. Serum was collected for ALT detection (5–7 mice per group). B) The liver and serum IL-33 levels in naïve mice and mice at day 6 post-infection were detected by an ELISA (6–7 mice per group). C) At 24 h post-infection, exogenous IL-33 (0.8 μg/ mouse in PBS) was i.p. injected into the infected mice daily until sacrifice at day 6. Representative microphotographs of hepatic H&E stain (6 dpi) are shown. The scale bars were 200 μm. D) Cumulative graphical representation of the histological scores. E) The number of Councilman bodies was counted in the H&E slides. F) Serum ALT was detected after IL-33 treatment (5–8 mice per group). Experiments were repeated for three times independently. Values were shown as mean ± SEM. A Two-tailed T-test was used for statistical analysis. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01.