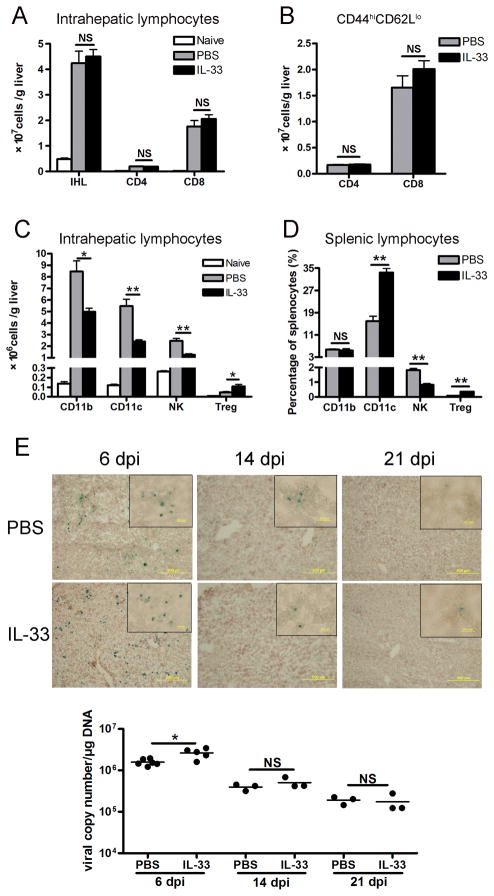
Figure 2. IL-33 had differential effects on liver-infiltrated cells.
B6 mice were i.v. injected with AdLacZ (3 × 109 PFU/mouse). At 24 h post-infection, exogenous IL-33 (0.8 μg/mouse in PBS) was i.p. injected into the infected mice daily until sacrifice at day 6 (5–6 mice per group). Livers were perfused and digested, and intrahepatic lymphocytes (IHL) were prepared by density gradient centrifugation. A) The numbers of IHL were counted under light microscopy. Hepatic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were gated on CD3+ cells and assayed by flow cytometry. B) Hepatic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were gated and analyzed for CD44 and CD62L expression by flow cytometry. The total numbers of CD4+CD44hiCD62Llo and CD8+CD44hiCD62Llo effector cells were shown. C) Hepatic infiltration of CD11b+, CD11c+, CD3−NK1.1+ and CD4+Foxp3+ T regulatory (Treg) cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. D) Percentages of CD11b, CD11c, NK and CD4+Foxp3+ Treg cells in the splenic lymphocytes were detected by flow cytometry. E) Viral clearance was assessed by the β-gal staining of liver frozen section as well as the viral copy numbers of liver tissues, respectively, at 6, 14, 21 dpi. Infected cells expressing β-gal activity were stained blue, whereas uninfected cells were counterstained red (3–5 mice per group). Original magnification: large panels 100 × (Scale bars: 200 μm); small panels 400 × (Scale bars: 20 μm). Experiments were repeated three times independently. Values were shown as mean ± SEM. A Two-tailed T-test was used for statistical analysis. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01.