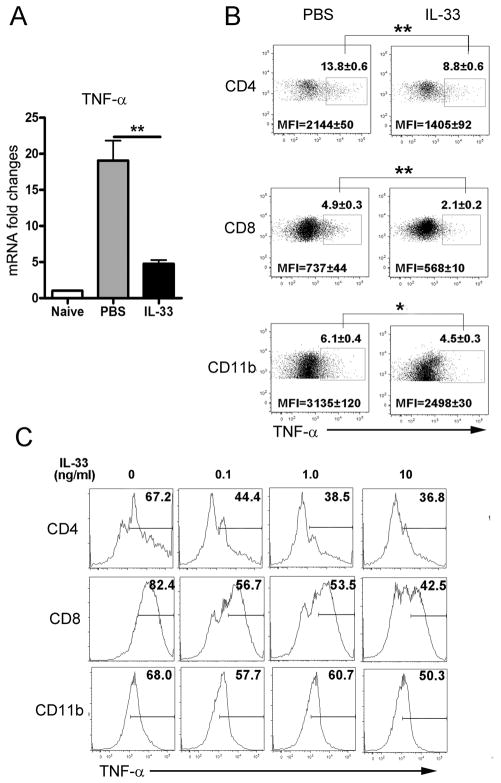
Figure 4. IL-33 inhibited hepatic TNF-α in viral hepatitis.
B6 mice were i.v. injected with AdLacZ (3 × 109 PFU/mouse) and at 24 h post-infection, exogenous IL-33 (0.8 μg/mouse in PBS) was i.p. injected into the infected mice daily until sacrifice at day 6 (3–5 mice per group). Liver tissues were collected for analysis of the gene expression, and IHLs were prepared for flow cytometry detection. A) Gene expression of hepatic TNF-α was analyzed by qRT-PCR. B) Expressions of TNF-α on hepatic CD4+ T, CD8+ T and CD11b+ cells were detected by flow cytometry. Percentages and mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) were shown as mean ± SEM. C) The IHLs isolated at day 6 post-infection were cultured with IL-33 (0, 0.1, 1 and 10 ng/ml, respectively) in complete RPMI medium plus IL-2 and IL-7 (10 ng/ml) for 48 h. Each treatment was performed in triplicate. PMA/ionomycin and GolgiStop were added to the cells at the last 4 h of the culture. Expressions of TNF-α on CD4+ T, CD8+ T and CD11b+ cells were detected by flow cytometry at the end of the culture. Experiments were repeated three times independently, and represented graphs were shown. A Two-tailed T-test was used for statistical analysis. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01.