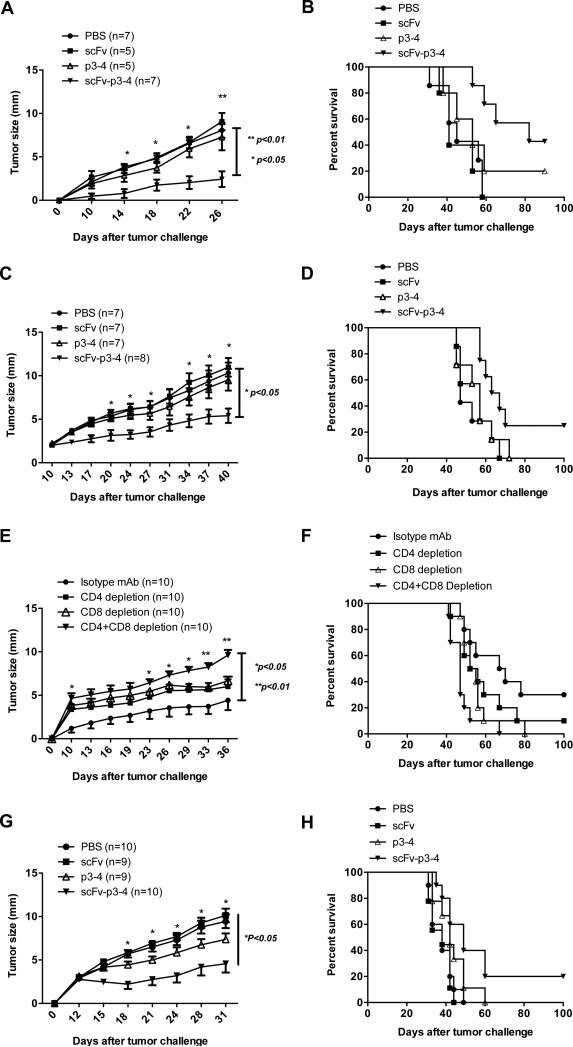
Figure 6. Reduced tumor burden and enhanced tumor-free survival upon scFv-p3-4 vaccination.
(A, B) BALB/c mice were vaccinated with scFv, P3-4 or scFv-p3-4 for 4 times at a 1-week interval. PBS-immunized mice were used as control. At day 28, immunized mice were challenged s.c. with 1×105 D2F2/E2 tumor cells. Tumor growth (A) and survival (B) were recorded. (C, D) BALB/c mice were challenged s.c. with 1×105 D2F2/E2 tumor cells. The mice were treated with scFv, P3-4 or scFv-p3-4 for 4 times at a 1-week interval when the tumor size (diameter) reached 2-3mm. Tumor growth (C) and survival (D) were recorded. (E, F) BALB/c mice were first injected intraperitoneally with anti-CD4 mAb (250μg), anti-CD8 (500μg) or isotype control mAb (250μg) on day -3. Mice were then immunized with different fusion proteins. The depletion mAbs or isotype control mAb was further injected 3 days before boost immunization. After 4 times immunization, mice were challenged s.c. with 1×105 D2F2/E2 tumor cells. Tumor growth (E) and survival (F) were recorded. (G, H) C57Bl/6 mice were challenged s.c. with 5×105 EO771/E2 tumor cells. Tumor-bearing mice were treated with scFv, P3-4 or scFv-p3-4 for 4 times at a 1-week interval when the tumor size (diameter) reached 2-3mm. Tumor growth (G) and survival (H) were recorded.