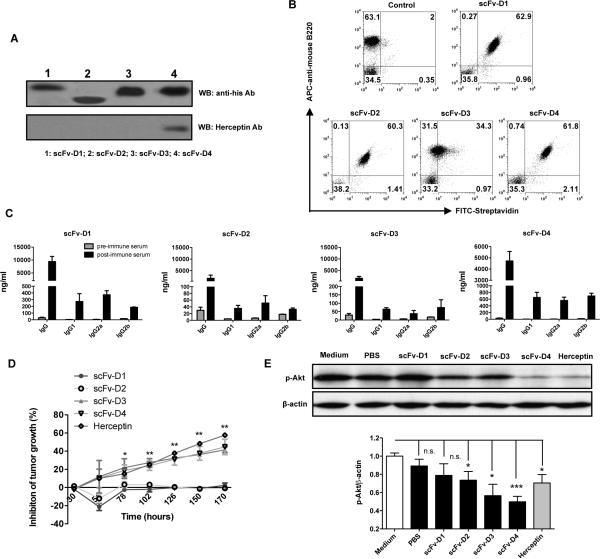
Figure 7. Abs elicited by targeting her-2/neu different ECD domains via CD19 scFV have differential anti-tumor effect in vitro.
(A) Purified fusion proteins scFv-D1, scFv-D2, scFv-D3 and scFv-D4 were blotted with his tag mAb or her-2/neu Ab. (B) For in vitro B cell binding, splenocytes were incubated with biotinylated scFv-D1, scFv-D2, scFv-D3, and scFv-D4 followed by APC-anti-mouse B220 and FITC-streptavidin. (C) Mice were immunized with scFv-D1, scFv-D2, scFv-D3 and scFv-D4 (50 μg/mouse) for 4 times at 1-week intervals. Sera were collected at day 28 and then measured for her2/neu-specific Abs by ELISA. (D) 1 × 104 SKBR-3 cells were placed into the wells of the Acea 16-well plates for 24 h. Heat-inactivated immune serum (1:20), pre-immune serum (1:20), or Herceptin (10 μg/ml) was added to wells and incubated for indicated times. The inhibition of tumor cell growth was calculated by measuring the relative decrease in current impedance among wells containing post-immune serum and wells containing pre-immune serum. (E) Immunoblotting of phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) in post-immune serum-treated (1:10 dilution), Herceptin (2 μg/ml) or medium-treated SKBR-3 cells. β-Actin served as loading control. Densitometric quantification is also shown (n=4). * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. n.s. not significant