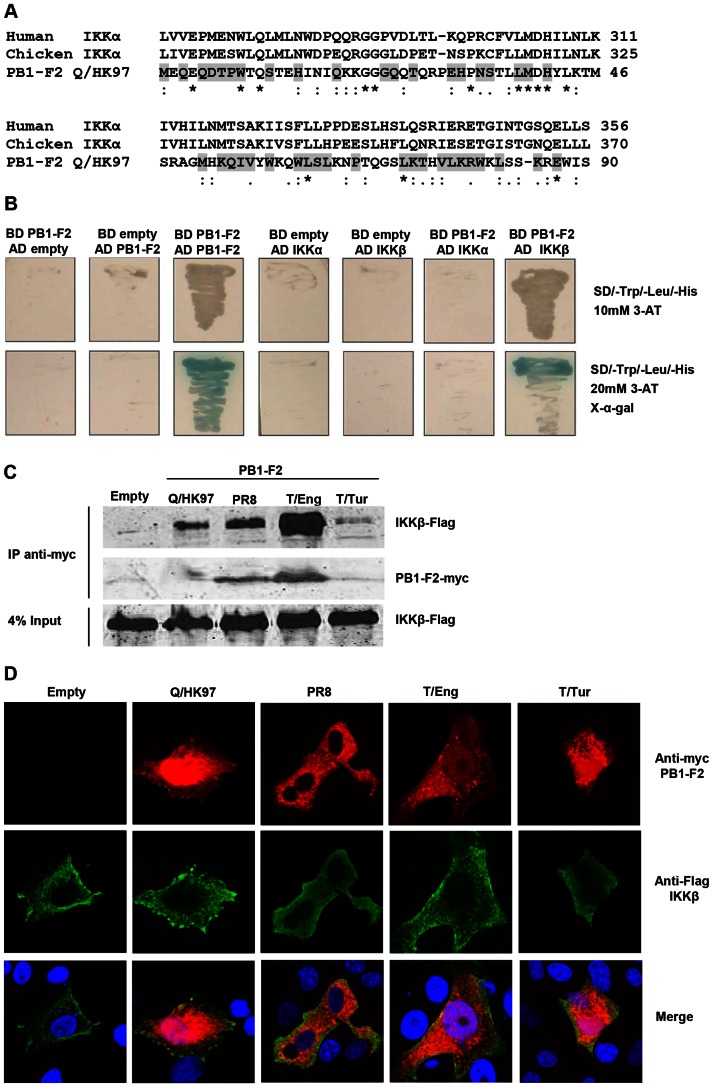
Figure 2. PB1-F2 has sequence similarity with IKKα and interacts with IKKβ.
A) Alignment of PB1-F2 Q/HK97 protein sequence with human and chicken IKKα using ClustalW (*denotes identical residues, : denotes conservative substitutions and. denotes semi-conservative substitutions). The grey shading denotes the conserved residues in PB1-F2 from PR8, T/Eng and T/Tur. B) Yeast cells were independently transformed with different combinations of pGADT7 (AD) and pGBKT7 (BD) constructs and plated on selective medium. Yeast cells co-transformed with BD PB1-F2 and AD PB1-F2 were used as a positive control for protein-protein interaction. C) Vero cells were transfected with the indicated constructs and forty eight hours after transfection, protein complexes were immunoprecipitated from cellular lysates using a monoclonal anti-myc antibody. Proteins in the immunoprecipitates and in the whole cell lysates (4% input) were evaluated by Western blot using anti-Flag and anti-myc antibodies. D) Vero cells were transfected with 300 ng of the different PB1-F2 expressing vectors and 300 ng of pcDNA3-IKKβ. The cellular localisation of the proteins was analyzed by confocal microscopy using anti-myc (PB1-F2, red) and anti-Flag (IKKβ, green) antibodies.