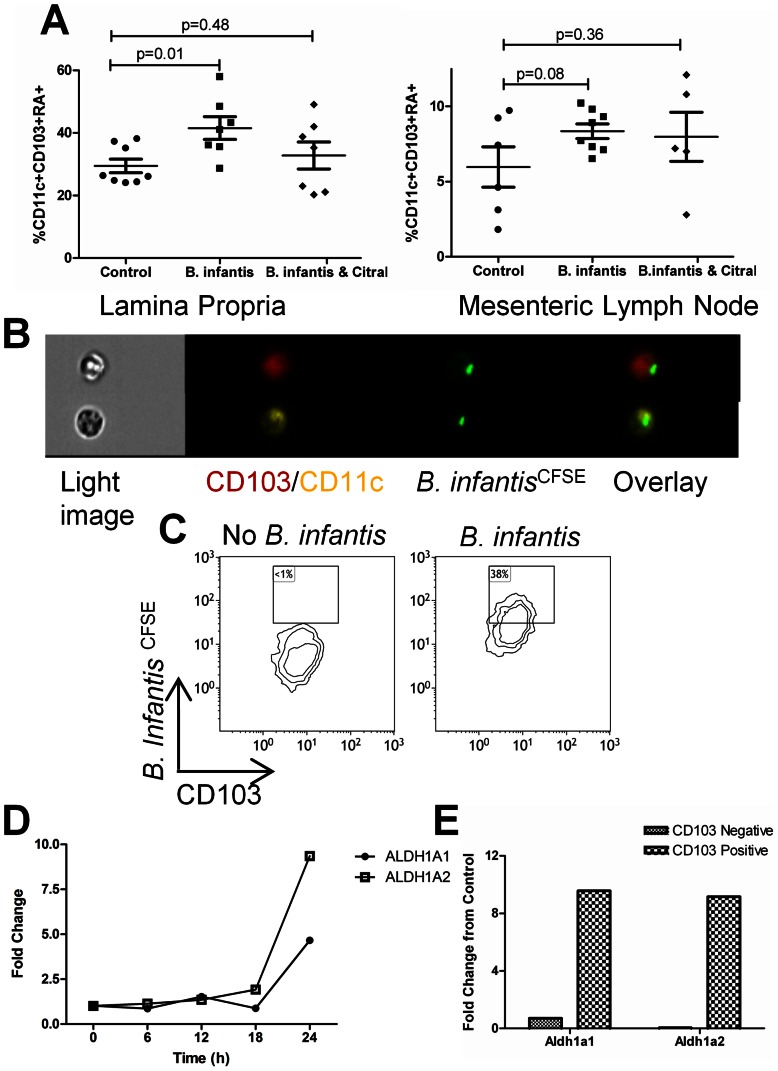
Figure 2. CD103+RALDH+ dendritic cells are elevated in the LP following B. infantis feeding.
Flow cytometric assessment of LP and MLN revealed that B. infantis feeding is associated with increased CD103+RALDH+ dendritic cells within the LP (n = 7), compared to the control group (n = 8), analysed using unpaired student t-tests (a). Citral blocked the increase in LP CD103+RALDH+ dendritic cells (n = 7). (b) Multispectral flow cytometry imaging identified CD103+ dendritic cells that efficiently bind CFSE-labelled B. infantis. (c) Flow cytometric analysis of CD11c+MHCII+CD103+ dendritic cells from the mucosa demonstrated that approximately 38% of CD103+ dendritic cells bound B. infantis. Isolated mucosal CD11c+ dendritic cells upregulate mRNA for RALDH enzymes following in vitro incubation with B. infantis (d), while the increase in gene expression is specific to CD103+ dendritic cells (e).