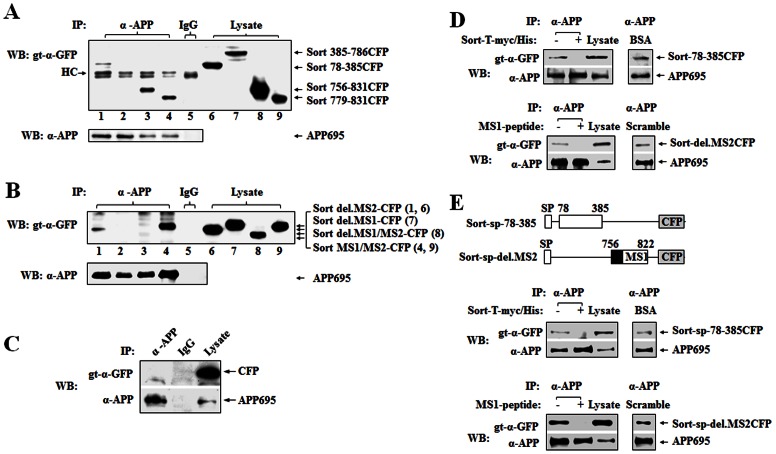
Figure 4. Mapping sortilin binding to APP.
(A) Identifying sortilin binding sites to APP. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with APP695-pcDNA3.1 (APP695) and Sort 78–385-CFP (lane 1) or Sort 385–786-CFP (lane 2), or Sort 756–831 (lane 3), or Sort 779–831-CFP (lane 4). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with mouse anti-APP, 22c11, (α-APP, lanes 1–4) and mouse IgG (mixed lysates, lane 5), and blotted with goat-anti-GFP (gt-α-GFP). Lysates were used as input (lanes 6–9). Sort 78–385CFP (61 kDa), Sort 385–786CFP (71 kDa), Sort 756–831CFP (35 kDa) Sort 779–831-CFP (32 kDa), APP695 (100 kDa) and IgG heavy chain (HC, 50 kDa) are indicated by arrows. (B) Determining sortilin C-terminal FLVHR motif (MS1) binding to APP. APP695 was used with Sort del.MS2-CFP (lanes 1, 6) or Sort del.MS1-CFP (lanes 2, 7) or Sort del.MS1/MS2-CFP (lanes 3, 8) or Sort MS1/MS2 (lanes 4, 9) for co-transfection. Co-IP was performed as (A). Sort del.MS2-CFP (34 kDa), Sort del.MS1-CFP (34 kDa), Sort-del.MS1/MS2-CFP (32 kDa), Sort MS1/MS2-CFP (33 kDa) and APP695 in precipitated samples and lysate are indicated by arrows. (C) Control for Co-IP using pECFP. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with pECFP/APP695. Co-IP was performed using α-APP and mouse IgG (IgG) as indicated. The blot was probed with α-GFP (upper) and re-probed with α-APP (lower). Lysate was used as input. APP695 and CFP (27 kDa) are indicated by arrows. Mouse IgG was used as a control for non-specific binding in all co-IP. (D and E) Sort-T-myc/His and MS1 peptide (CGGRFLVHRYSVLQQ; Peptide-2.0, Chantilly, VA) corresponding to the amino acids 783–797 of sortilin (GenBank Accession No. NM_002959) prevent sortilin N or C terminal constructs binding to APP in the competition binding assay, respectively. Sort-78–385CFP and Sort-del.MS2CFP (D) and two new sortilin constructs (termed Sort-sp-78–385-CFP and Sort-sp-del.MS2CFP) created by overlapping PCR and cloned in pECFP (E) were used in the competition binding assays. The integrity of the constructs was confirmed by DNA sequencing. To purify Sort-T-myc/His, HEK293 cells growing in 3×10 cm culture dishes were transfected with Sort-T-myc/His for 48 h. Cells were harvested in cold PBS containing 1 mM PMSF and protease inhibitor (Roche), sonicated on ice and centrifuged at 15000 rpm at 4°C for 10 minutes. The supernatant was loaded into Ni-NTA column (Qiagen) and eluted in elution buffer after washing. The elute protein was concentrated by Amicon Ultra- Centrifugal Filters (Millipore) and the protein was recovered in 50 µl of PBS pH 8, containing 1 mM PMSF and protease inhibitor. For competition binding assays, HEK293 cells (1×10 cm dish) were transfected with APP695 or each sortilin construct for 48 hours and harvested for preparing cell lysates. The lysate containing APP695 was incubated with 50 µl (+) of the purified Sort-T-myc/His protein or with 10 µM (+) of MS1 peptide at 4°C for 1 hour and then combined with the lysate containing Sort-78-385CFP or Sort-del.MS2CFP or Sort-sp-78-385-CFP or Sort-sp-del.MS2-CFP, and the incubation was continued for 2 hours at 4°C with rotation. The lysates were then immunoprecipitated with α-APP and blotted for Sort-78-385 and Sort-del.MS2 by gt-α-GFP, respectively. Cell lysate was used as input. Scramble MS1 peptide (Scramble, 10 µM) and BSA (10 µM) were used as control for non-specific competition. Sortilin constructs and APP695 from co-IP samples and inputs are indicated by arrows.