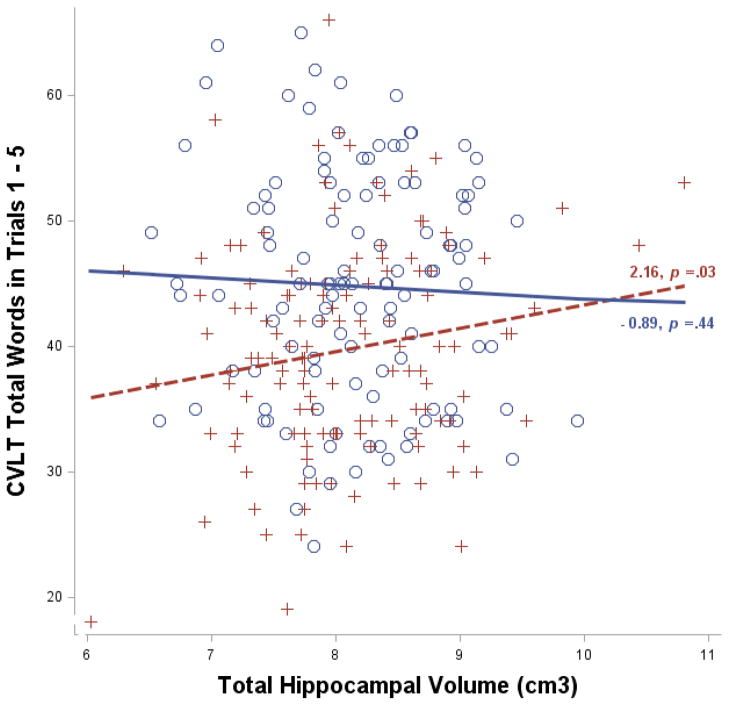
Fig. 1.
Relationship between California Verbal Learning Test (CVLT) total number of words in trials 1 – 5 and bilateral hippocampal volume (in cubic centimeters, adjusted for age and estimated total intracranial volume) among individuals with high (blue circles and solid line) and low (red crosses and dotted line) cognitive reserve. High and low reserve individuals are those in the upper and lower quartiles according to their age 20 general cognitive ability, respectively. The slope estimates denote the change in CVLT score as a function of one cm3 increase in hippocampal volume.