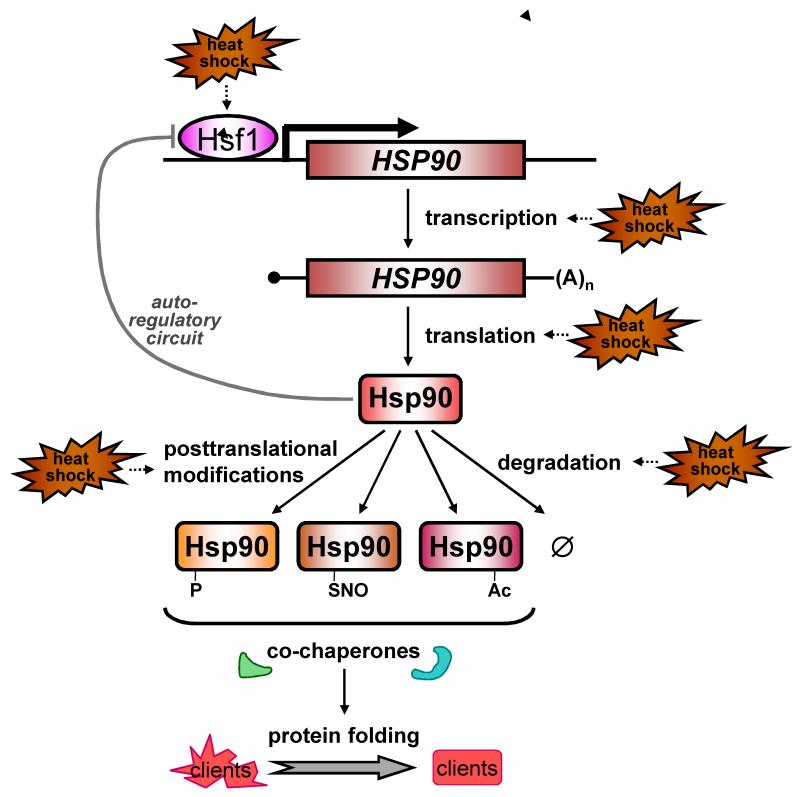
Figure 2. Hsp90 levels and activity are regulated at multiple levels.
(see text). Hsp90 transcription is regulated by the heat shock transcription factor (Hsf1), the activation of which is negatively regulated by Hsp90 via an autoregulatory loop13 that involves a physical interaction between Hsp90 with Hsf1 (Leach et al. unpublished). During heat shock, yeast HSP mRNAs may be preferentially translated and Hsp90 turnover might also be modulated (see text). Hsp90 activity is controlled by posttranslational modifications such as phosphorylation, s-nitrosylation and possibly acetylation. These changes influence Hsp90 interactions with specific co-chaperones, and hence affect the folding of specific subsets of client proteins. Furthermore, after proteotoxic stress changes in Hsp90 availability, mediated by altered HSP90 expression and changes in the amount of Hsp90 associated with unfolded proteins, is predicted to affect interactions with Hsp90 client proteins13.