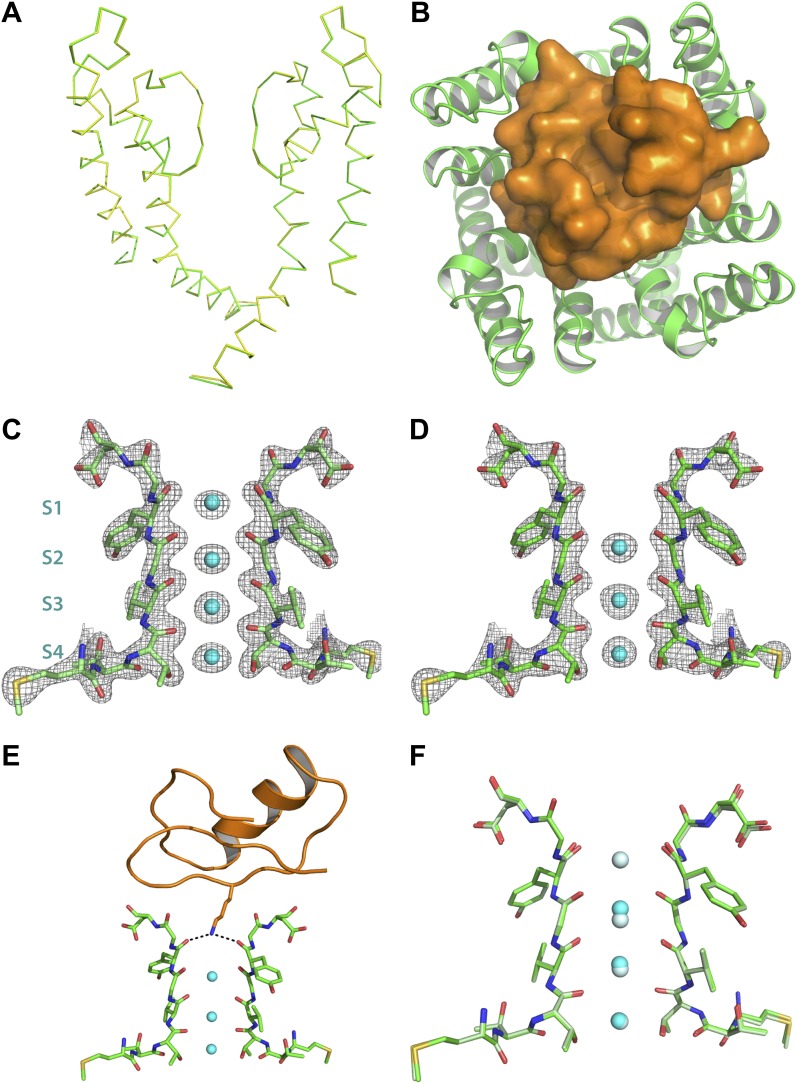
Figure 6. Structure of the toxin-channel complex.
(A) Side view showing pore domains from two diagonal subunits from paddle chimera (yellow; PDB ID 2 R9R; Long et al., 2007) and the toxin-channel complex (green) in α carbon trace. They have been superimposed by RMSD superposition of the main chain atoms from residues Met321-Thr414. (B) The tetrameric pore domain in the toxin-channel complex is shown in green ribbon trace from an extracellular view looking into the molecule. The bound CTX is shown in surface rendition in orange. (C) Side view of the selectivity filter (two diagonal subunits, molecule B) from the paddle chimera structure shown in stick rendition with the K+ ions shown as cyan spheres. Sites S1 through S4 in the selectivity filter are labeled (labels on left side) in cyan. A weighted 2Fo − Fc electron density map contoured at 3σ is shown in wire mesh. (D) Side view of the selectivity filter (two diagonal subunits, molecule B) from the toxin-channel complex is shown in stick rendition with the K+ ions shown as cyan spheres. A weighted 2Fo − Fc electron density map contoured at 3σ is shown in wire mesh. (E) The selectivity filter from the toxin-channel complex is shown in stick rendition with the K+ ions shown as cyan spheres. Also shown is the bound CTX molecule in orange ribbon trace and the side chain of the Lys27 residue in stick rendition. Close contact between the amino headgroup and the carbonyl oxygen in the selectivity filter are shown in dotted lines. (F) RMSD superposed structures of the selectivity filter regions (same regions as shown in Figures 6C,D) of the paddle chimera (pale green) and the toxin-channel complex (green) shown in stick rendition. The superposition was done using the main chain atoms from residues Met321-Thr414. The K+ ions in the paddle chimera structure are shown in light blue and those in the toxin-channel complex in cyan.
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Electron density for the side chain of Lys27 of CTX in the paddle chimera–CTX complex.