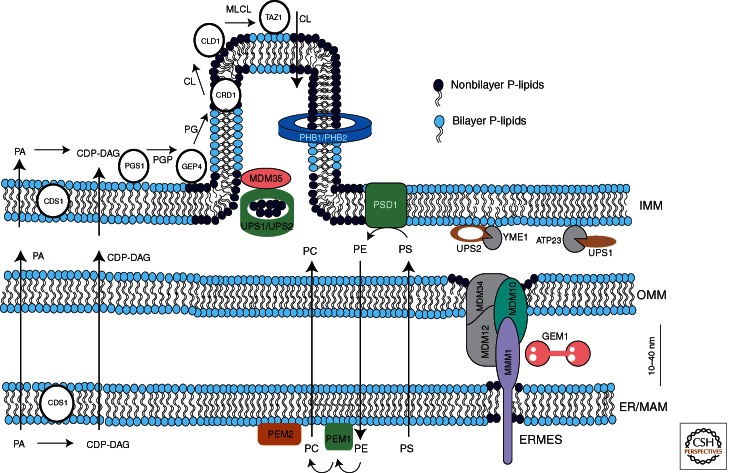
Figure 3.
Components involved in translocation of phospholipids to and within mitochondria of yeast. The directions of lipid translocation are indicated by arrows. While PS and PC are imported into mitochondria, a large portion PE is exported. Upon import the majority of PS is converted to PE by Psd1p. Decarboxylation of PS to PE in mitochondria and methylation of PE to PC in the ER are sufficient for supplying cells with PE and PC even in the absence of external ethanolamine or choline. Similar to PS and PC, PA and CDP-DAG also have to be imported into mitochondria where they are required for CL synthesis. The pathway of CL synthesis in the IMM starts with CDP-DAG and is completed during several steps by a multienzyme cascade. A small portion of CL is exported to the OMM. The ERMES complex containing gene products of MDM10, MDM34, MDM12, and MMM1 tethers ER and mitochondria. In mammalian cells, Mfn1/2 seem to have a similar function. ERMES associates with the GTPase GEM1, cycling between ERMES bound and free form. UPS1/UPS2 interact with Mdm35p and regulate the mitochondrial levels of PE and CL. UPS1 and UPS2 are degraded by ATP23 and YEM1, respectively. Prohibitin ringlike structures made from two proteins PHB1/2 contribute to the formation of PE and CL clusters in the IMM. For a detailed description of biosynthetic and translocation processes and components involved, see text.