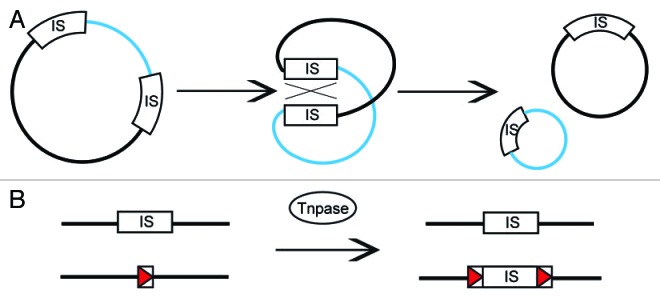
Figure 2. Homologous recombination and transposition: two IS-mediated gene inactivation patterns identified in A. salmonicida. (A) Homologous recombination events involving two IS in a plasmid can lead to deletions. Such events are transposase-independent and can occur because the two IS are identical. In such cases, the DNA fragment bearing the replication origin is replicated and propagated, while the other fragment is deleted. This deletion pattern occurs in pAsa5 plasmid and is mediated by IS11 leading to the deletion of the TTSS locus.14(B) A transposition event involving a single IS can lead to gene inactivation. An IS can use its transposase (Tnpase) to insert at an insertion site (red arrow). The transposition causes the duplication of the insertion site. In A. salmonicida, ISAS1 and ISAS2 can transpose in the vapA and abcA genes, which are essential for the proper assembly and display of the A-layer.10,11 In the case of ISAS1 and ISAS2, the transposition is coupled with duplication, leaving a copy of the IS on the donor strand.9
