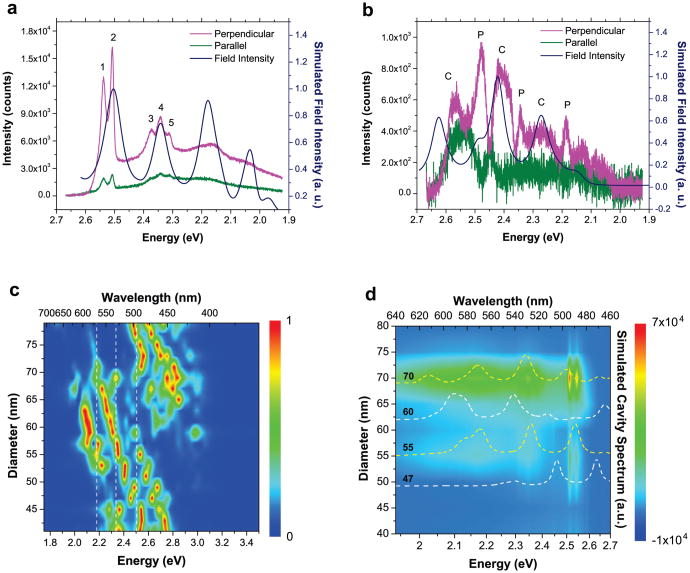
Figure 3. Polarization-selective spectra for resonant and nonresonant plasmonic silicon devices.
a, Polarization-resolved hot-luminescence spectra for a resonant-sized plasmonic cavity coupled silicon nanowire (d = 70 nm) showing anisotropic emission polarized predominantly perpendicular to the nanowire's long axis. The strong emission bands are exactly overlapped with the calculated energy-dependent field intensity inside the cavity showing resonances. b, The same measurement procedure was followed for a nonresonant-sized plasmonic cavity-coupled silicon nanowire device (d = 50 nm). Both the cavity modes (“C”) and hot-luminescence bands (“P”) corresponding to phonons with high density of states are revealed on the perpendicularly polarized emission spectrum. The cavity modes are confirmed by the calculated cavity field intensity as a function of energy. c, Calculated field intensity spectra inside the plasmon cavities as a function of nanowire diameter. The white dashed lines indicate the three strong hot-luminescence bands, corresponding to the phonon modes with high density of states. d, Experimental size-dependent photoluminescence spectra for the nanowires with diameter ranging from 40 to 80 nm. Calculated spectra for cavity field intensity (dashed lines) are also plotted to show the resonant and non-resonant conditions between the cavity modes and the highly emissive hot-luminescence bands.