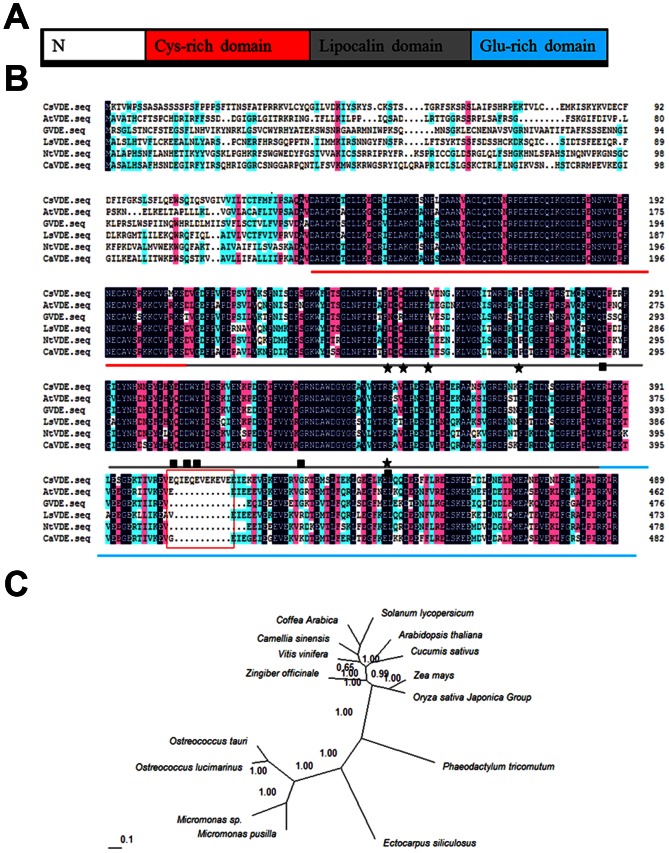
Figure 1. Amino acid sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis of CsVDE and homologous proteins.
(A) Schematic description of CsVDE domains. (B) Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences of VDE in different plants. Red lines indicate the VDE Cys-rich domain; Gray lines indicate the Lipocalins domain; Blue lines indicate the Glu-rich domain. The important residues for pH switch are marked with black stars and the putative active site residues with black squares reference from Arnoux et al. (2009) [11]. Arabidopsis thaliana VDE (accession No. AEE28305), Zingiber officinale VDE (accession No. AAX59986), Lactuca sativa VDE (accession No. AAC49373), Nicotiana tabacum VDE (accession No. AAC50031), Coffea arabica VDE (accession No. ABB70816) sequences are shown. Black indicates 100% homology of the amino acid. Red indicates 75% homology of the amino acid. Green indicates 50% homology of the amino acid. (C) Phylogenetic analyses of selected VDEs. Phylogenetic studies were carried out using MrBayes3.1.2 and viewed with the TreeView package. All the trees were obtained with 200,000 generations for the chains, a sample frequency of a 10, and a burn in of 5,000 (ngen = 200000; Samplefreq = 10; burnin = 5,000). Camellia sinensis VDE (accession No. AAL67858), Vitis vinifera VDE (accession No. XP_002267152), Osterococcus tauri VDE (accession No. XP_003083515), Ostreococcus lucimarinus VDE (accession No. XP_001421704), Micromonas sp. VDE (accession No. XP_002503106), Micromonas pusilla VDE (accession No. XP_003061123), Ectocarpus siliculosus VDE (accession No. CBJ26509), Phaeodactylum tricornutum VDE (accession No. XP_002178643), Oryza sativa Japonica Group VDE (accession No. AAL83562), Zea mays VDE(accession No. NP_001147756), Solanum lycopersicum VDE (accession No. ACM92036).