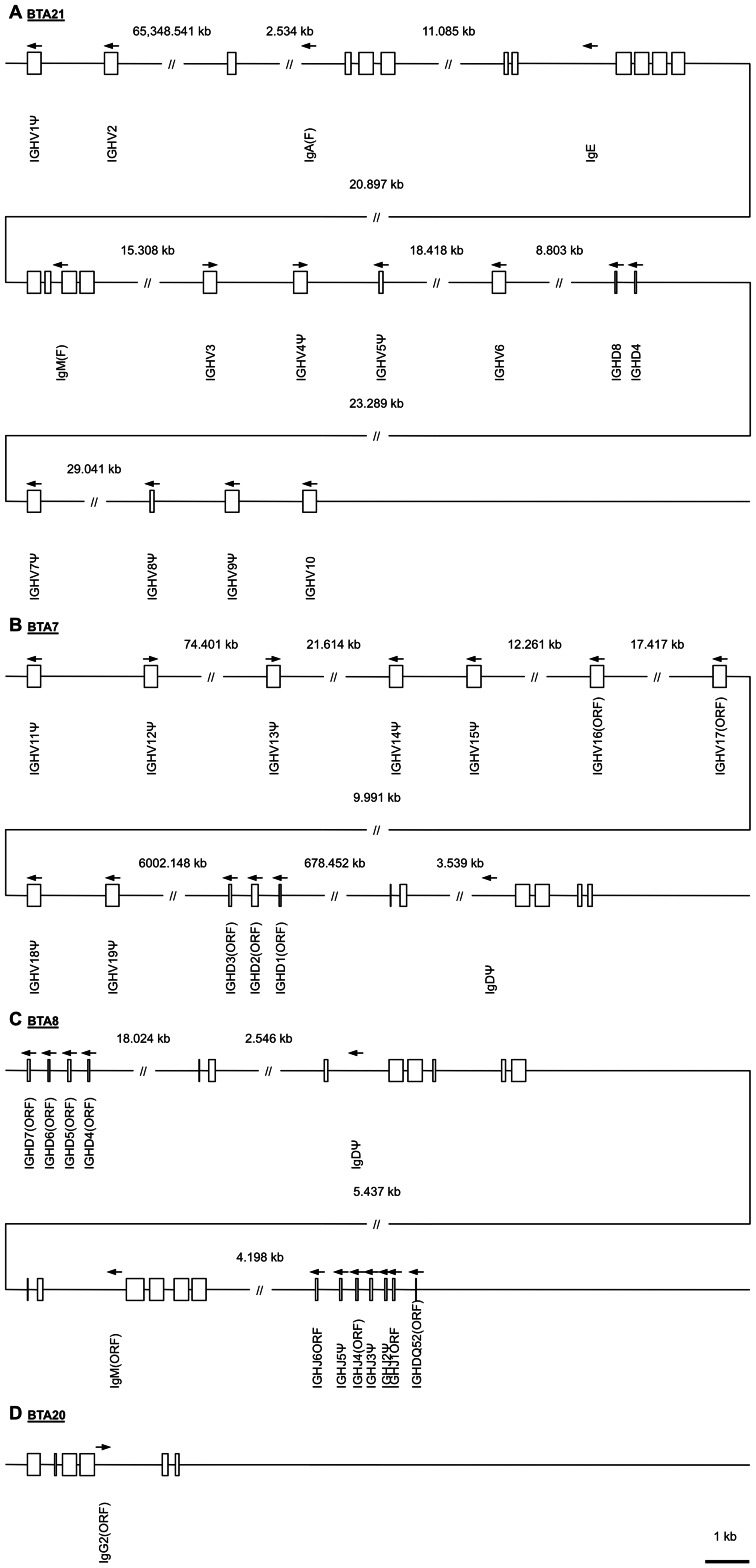
Figure 1. Chromosomal organization of variable (IGHV), diversity (IGHD), joining (IGHJ) segments, and the constant regions of the heavy chains.
The physical map displays the order of functional segments (F), pseudogenes (Ψ), and open reading frames (ORF). Classification to “functional” includes an ORF without stop and exhibition of conserved amino acid residues as well as no defects in splicing signals, recombination signal sequences (RSS) or regulatory elements. ORF are defined by alterations in the splicing signals, recombination signal sequences, and/or regulatory elements. In addition, changes to conserved amino acid residues, which may lead to misfolding were included in the ORF classification. Functional elements on orphon localizations are highlighted with ORF in parenthesis (ORF) [38], [39]. Pseudogenes possessed stop codons, frameshifts or mutations of the spacer lengths within the first three nucleotides of the heptamer as well as in three consecutive adenosines residues within the nonamer abolish the recombination [40], [41]. In addition, fragmented loci were also defined as pseudogenes. Arrows indicate the transcription direction.