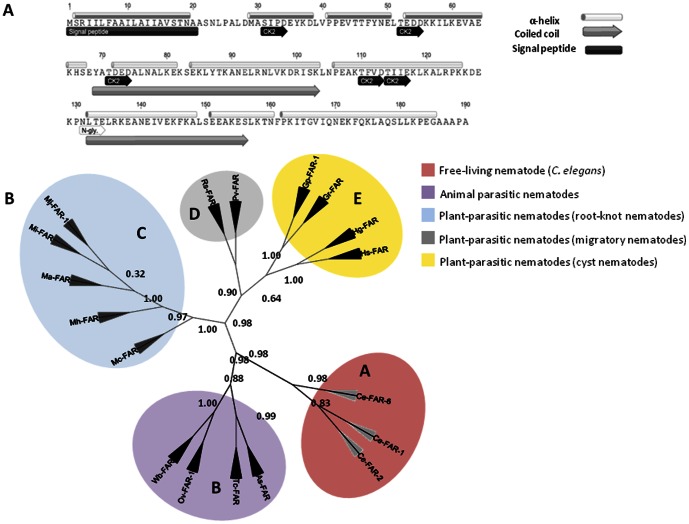
Figure 1. Mj-FAR-1 characterization.
A. Primary and secondary structure analysis of predicted Mj-FAR-1. A putative hydrophobic leader/signal peptide, as predicted by the SignalP program is shown at the N terminus along with a cleavage site between two alanine residues at position 20–21. Consensus N-linked glycosylation site (N-gly) and the consensus casein kinase II phosphorylation sites (CK2) are indicated. Secondary structure analysis through Jpred predicts a predominantly alpha-helical conformation (gray cylinder) with coiled-coil structures (gray arrow) as shown. B. Phylogenetic tree of Mj-FAR-1 with other nematode FAR proteins. The tree was constructed with FAR protein sequences of: C. elegans (Ce-FAR-1, Ce-FAR-2 and Ce-FAR-6) belong to group A, human parasitic nematodes O. volvulus (Ov-FAR-1) and W. bancrofti (Wb-FAR), animal parasitic nematodes A. suum (As-FAR) and T. canis (Tc-FAR), and plant-parasitic nematodes, M. javanica (Mj-FAR-1), M. incognita (Mi-FAR), M. arenaria (Ma-FAR), M. hapla (Mh-FAR) and M. chitwoodi (Mc-FAR), cyst forming nematodes G. pallida (Gp-FAR-1), G. rostochiensis (Gr-FAR), H. glycines (Hg-FAR), H. schachtii (Hs-FAR) and migratory endoparasites P. vulnus (Pv-FAR) and R. similis (Rs-FAR). Bootstrap values are shown at each node. 1,000 bootstrap replicates were obtained, with nearly the same results, and only a single tree retrieved from the phylogenetic relationship analysis is shown. Five clusters in the phylogenetic tree have been arbitrarily assigned the names A, B, C, D and E.