FIG. 4.
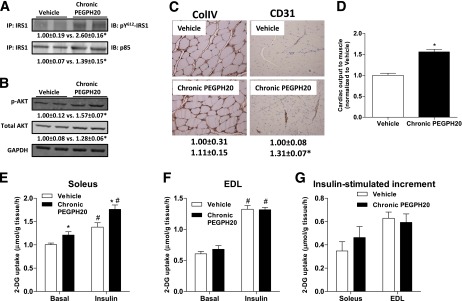
Effects of chronic PEGPH20 on muscle in DIO mice. A: Gastrocnemius muscle was collected at the end of the ICv. Tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS1 and IRS1-associated p85 were assessed by immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. B: Protein expression of Akt and phosphorylated Akt was assessed by Western blotting in muscle homogenates. C: Protein expression of collagen IV (ColIV) and CD31 were measured by immunohistochemistry in gastrocnemius muscle collected at the end of the ICv. ColIV expression was measured by the integrated intensity of staining. Muscle vascularity was determined by counting CD31-positive structures. D: Cardiac output to muscle was assessed by microspheres that were injected to the arterial catheter after the ICv. Data were normalized to vehicle. n = 4–8. *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle. E–G: Soleus and EDL muscles were isolated from mice chronically treated with vehicle or PEGPH20 for 24 days. In vitro glucose uptake was measured using 2-[3H]deoxyglucose on day 27. n = 7–9. *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle and #P < 0.05 vs. basal. All data are represented as mean ± SEM. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (A high-quality color representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)
