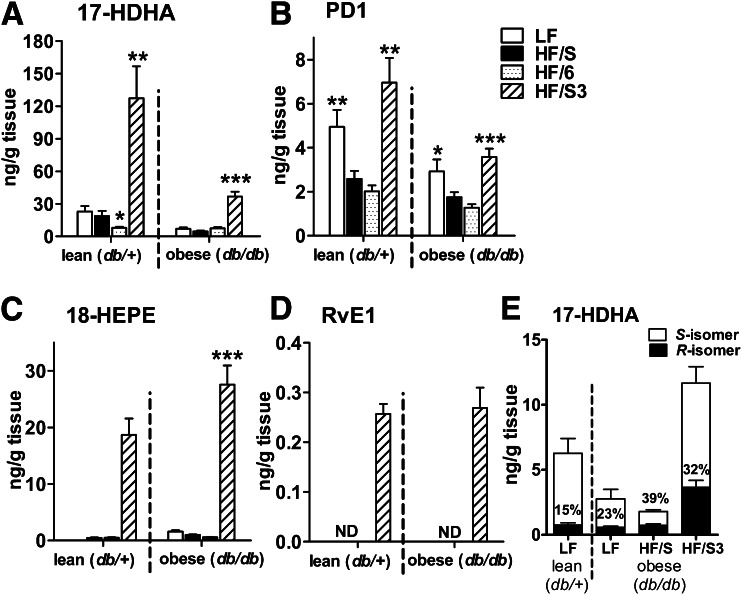
FIG. 5.
Dietary n-3 PUFA treatment increases synthesis of n-3 PUFA–derived SPMs and their precursors in the adipose tissue of genetically obese mice. Lipid mediator concentration was determined in gonadal fat pads of db/+ and db/db mice fed the LF, HF/S, HF/6, or HF/S3 diet using LC-MS/MS. HF/S3 treatment of db/db animals significantly increased the adipose tissue concentration of DHA-derived 17-HDHA (A) and PD1 (B) as well as EPA-derived 18-HEPE (C) and RvE1 (D) (n = 10 animals per group). Dietary effects within db/db and db/+ animals were compared with the respective HF/S groups. (E) Stereoselective analysis using chiral-based LC-MS/MS revealed 17S-HDHA as the main naturally occurring stereoisomer in gonadal adipose tissue of db/+ and db/db animals. The percentage of 17R-HDHA calculated from the total 17-HDHA in adipose tissue was increased after HF feeding (n = 10 animals per group). All data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. ND, not detected.