Figure 2. N-linked glycosylation in M. voltae.
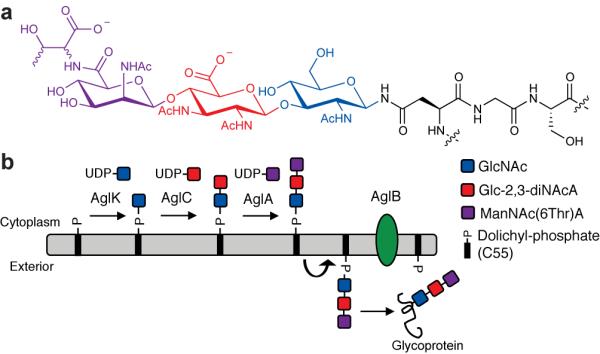
(a) The M. voltae N-linked glycan is ManNAc(6Thr)A-β1,4-Glc-2,3-diNAcA-β1,3-GlcNAc, where Glc-2,3-diNAcA is 2,3-diacetamido-2,3-dideoxy-d-glucuronic acid and the stereochemistry of the threonine residue is currently unknown. (b) N-linked glycan biosynthesis in M. voltae is initiated in the cytoplasm by the AglK-catalyzed transfer of GlcNAc to the membrane bound acceptor Dol-P. AglC transfers Glc-2,3-diNAcA to Dol-P-GlcNAc to form a β-1,3 linkage, presumably followed by the action of AglA. The resulting Dol-P linked trisaccharide is flipped from the cytoplasm to the exterior of the cell by a currently unidentified flippase and then transferred en bloc to a recipient protein by the OTase, AglB.
