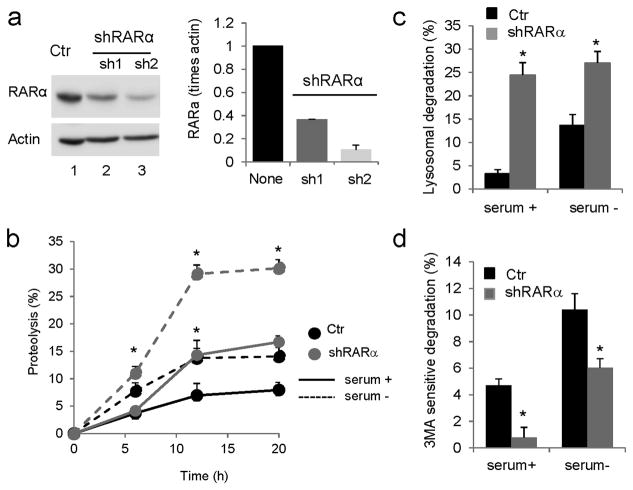
Figure 1. Effect of knockdown of RARα on intracellular turnover of long-lived proteins.
(a) Knockdown of RARα in NIH3T3 mouse fibroblasts was conducted using two different shRNAs, sh1 and sh2. Ctr: control. Left: Representative immunoblot. Actin is shown as loading control and full-length blots are shown in Supplementary Figure 21. Right: Levels of RARα in control and knockdown cells determined by densitometric quantification of immunoblots represented by the one shown on the left. Values are normalized for actin and expressed as times control (none) values. (n=3) (b) Rates of degradation of long-lived proteins in control and RARα-knockdown cells maintained in the presence or absence of serum for 12 h. Values are expressed as percentage of proteolysis. (n=3) (c, d) Percentage of lysosomal (c) and macroautophagy (d) degradation in cells assayed as in b, but treated with inhibitors of lysosomal proteolysis (c) or with 3-methyladenine to block macroautophagy (d). Values are expressed as percentage of total protein degradation sensitive to the lysosomal inhibitors (n=3). All values are mean±S.E. and differences with control are significant for *p<0.05.