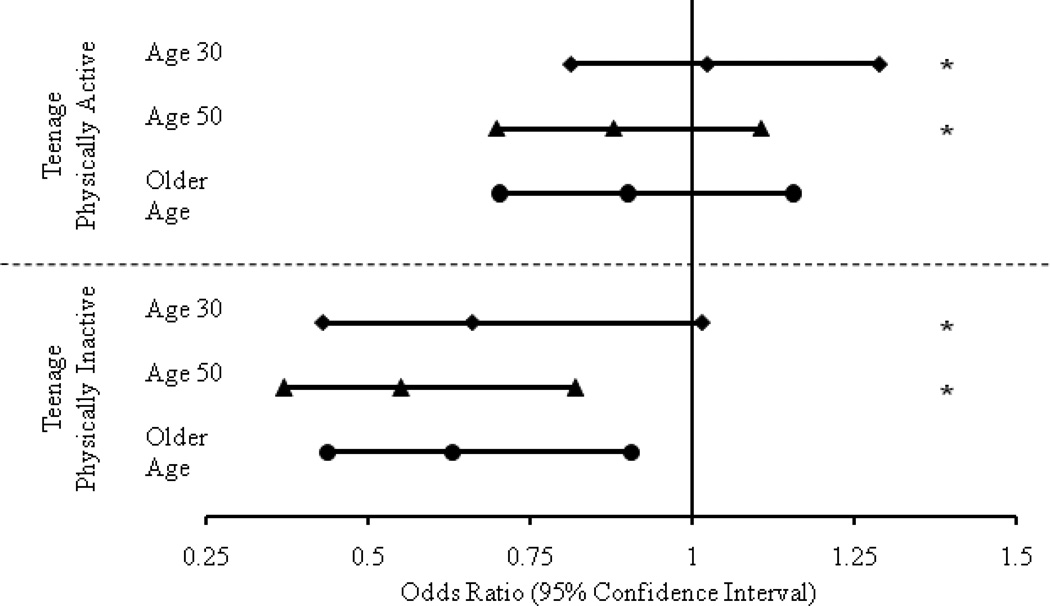
Figure 1. Adjusted odds of cognitive impairment in older women who were physically active versus inactive over the life course, stratified by teenage physical activity status.
* Interaction terms are significant for Age 30 and 50: Teenage*Age 30: p=0.004; Teenage*Age 50: p=0.011
** The models were adjusted for:
Age 30: education, diabetes, depressive symptoms, smoking, BMI
Age 50: age, education, marital status, diabetes, depressive symptoms, smoking, BMI
Late Life: age, education, marital status, diabetes, hypertension, depressive symptoms, BMI