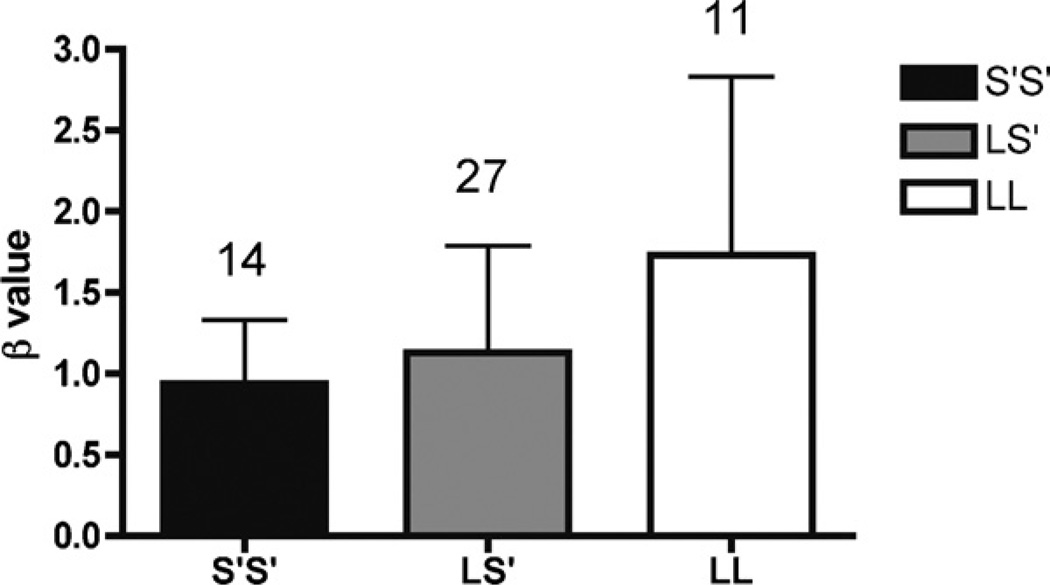
Fig. 1.
Male and female participants. Low β indicates higher impulsivity. The effects of 5-HTTLPR genotype on impulsive response style (β) in male (N= 38) and female (N= 14). Individuals who had the S′/S′ genotype were more impulsive than individuals with the L/S′ genotype, who in turn were more impulsive than those with the L/L genotype (p = 0.026). The number of participants in each group is displayed on top of the bars, and the Whiskers indicate standard deviations.