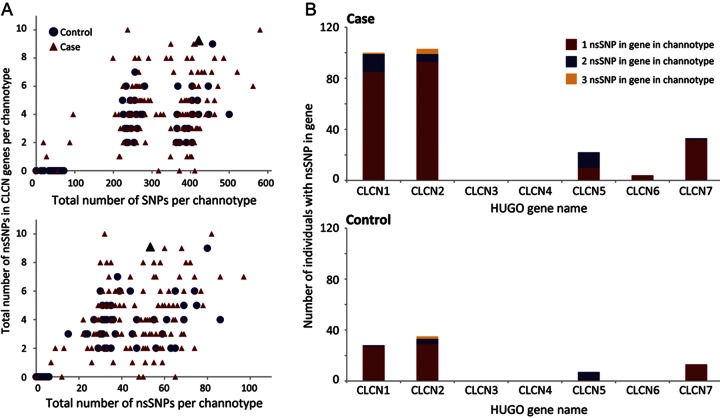
Figure 1. Genetic variation in CLCN genes among individuals with sporadic idiopathic epilepsy compared with neurologically normal controls.
(A) Parallel exomic sequencing reveals that the total number of individuals with structural variants (nsSNPs) in CLCN genes is greater in an idiopathic epilepsy (IE) population compared with controls. Scattergrams of all individuals within each cohort show the total number of CLCN nsSNPs per individual plotted against number of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (top panel) or nsSNPs contained in their channotype (bottom panel). The number of nsSNPs in the CLCN genes is independent of total SNP and nsSNP load in an individual channotype. The proband with the de novo truncation is identified as a black triangle. (B) Histograms show mutation burden of CLCN1–7. Individuals with IE have 3 times as many nsSNPs in CLCN1 and CLCN2, including a small number of individuals with 2 or more nonsynonymous variants within the same channel gene. No nsSNPs were identified in the CLCN3 or CLCN4 genes.