Figure 1. Examples of MRI findings.
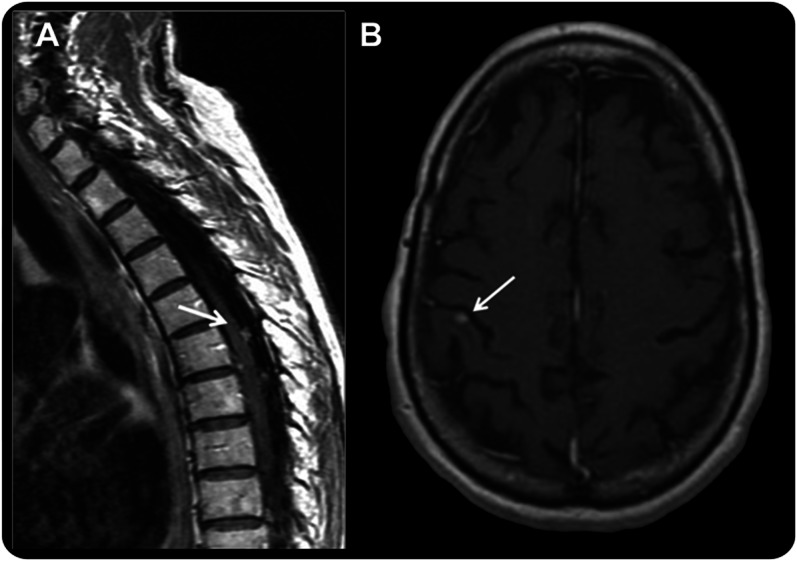
(A) Sagittal T1 postgadolinium image of the spine showing typical enhancing subarachnoid nodules considered in this study as unequivocal for the diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastasis (LM). (B) Axial T1 postgadolinium image of the brain in a patient with non–small cell lung cancer who developed progressive, mild gait ataxia and was found to have superficial, small, contrast-enhancing lesions (arrow). Given the superficial location of the lesions, the MRI was considered suspicious but not unequivocal for LM because the lesion seems intraparenchymal, posing a diagnostic problem. The CSF analysis showed 1 white cell/mm3 and negative cytology, but CSF circulating tumor cell (CTC) analysis was positive (0.13 CTC/mL). The lumbar puncture was repeated 3 weeks later, and both conventional cytology and CSF CTCs were positive, confirming the diagnosis of LM, as anticipated by the CSF CTC results.
