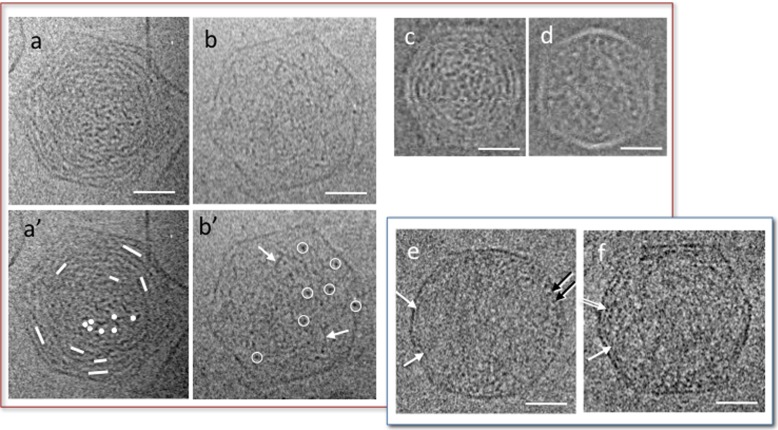
Fig. 3.
Conformations observed by cryo-TEM of partially filled capsid in the presence of mono- and di-valent ions and quenched at room temperature (a–d) and at 4 °C (e, f). Cholesteric (a, c) and isotropic (b, d) organisations observed in bacteriophage T5 (a, b) and T3 (c, d, reproduced from [37]) in Tris 10 mM, NaCl 100 mM, MgCl2 1 mM, CaCl2 1 mM (T5) and Tris 10 mM, NaCl 200 mM, MgCl2 1 mM (T3). In the cholesteric conformations the orientation of the DNA segments (underlined by dots and lines in a′) rotates between the central region and the periphery, in a double twist organisation. In the isotropic conformation, DNA is randomly oriented. DNA segments locally perpendicular to the observation plane are circled in white (b′). Some of the DNA segments locally oblique or parallel to the observation plane are pointed by white arrows. e, f Partially filled capsids of T5 in the same ionic conditions (Tris 10 mM, NaCl 100 mM, MgCl2 1 mM, CaCl2 1 mM), quenched after 15 min stabilisation at 4 °C. DNA segments locally visible in transverse view (dots, black arrows) or oblique or longitudinal views (white arrow) accumulate at the periphery, forming a monolayer in some regions. A double layer is also visible locally (double arrow). Scale bars = 20 nm