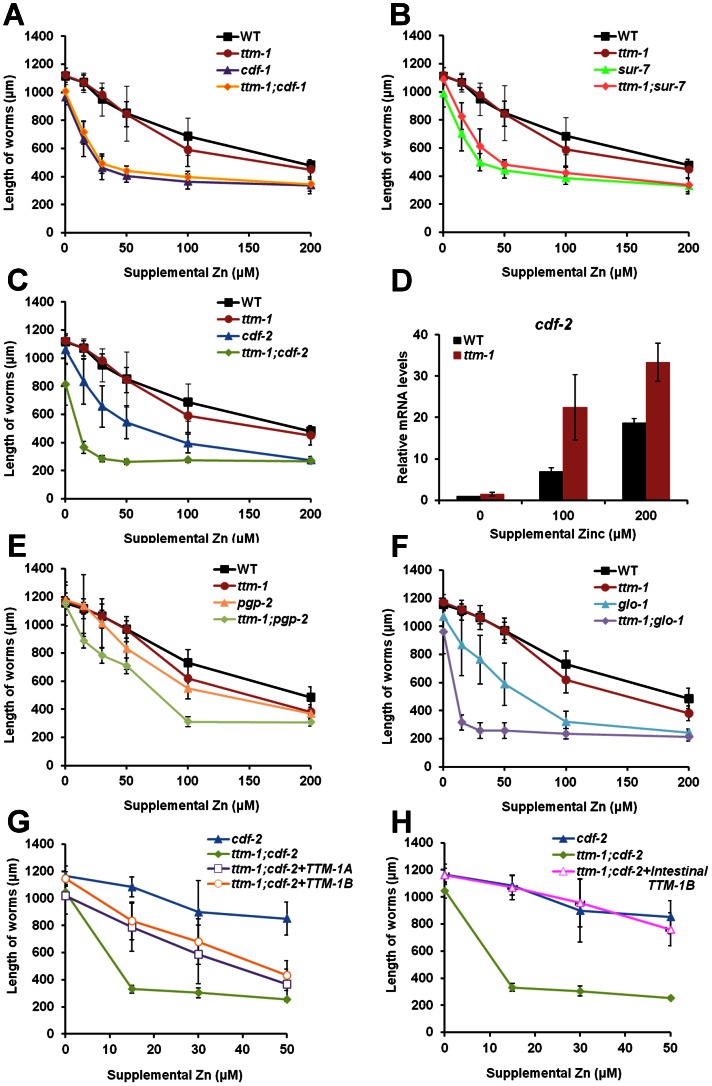
Figure 7. Role of ttm-1 in zinc detoxification.
(A,B,C,E,F) Zinc sensitivity was determined by analyzing the length of animals cultured from the first larval (L1) stage with the indicated concentrations of supplemental zinc. The length of worms was analyzed using microscopy and imageJ software (n = 20). The alleles were ttm-1(ok3503), cdf-1(n2527), sur-7(ku119), cdf-2(tm788), glo-1(zu391), and pgp-2(kx48). (D) Analysis of cdf-2 mRNA levels in wild-type and ttm-1(ok3503) animals cultured with the indicated concentrations of supplemental zinc. The Y-axis represents the fold changes of mRNA levels, and the bars indicate the average ± SEM of two independent experiments. The mRNA level in wild-type animals at 0 µM supplemental zinc was set equal to 1.0, and the other samples were relative to that sample. Compared to wild-type animals, cdf-2 mRNA levels were elevated in ttm-1 mutant animals cultured with supplemental zinc in both independent trials, indicating this is a reproducible result. However, the combined data did not reach statistical significance at the level of p<0.05 because the values of the fold changes varied between the experiments. (G–H) Zinc sensitivity of cdf-2(tm788), ttm-1(ok3503);cdf-2(tm788), and transgenic ttm-1(ok3503);cdf-2(tm788) animals expressing TTM-1A::GFP driven by the ttm-1a promoter [Pttm-1a::TTM-1A::GFP] (G), TTM-1B::GFP driven by the ttm-1b promoter [Pttm-1b::TTM-1B::GFP] (G), or TTM-1B::GFP driven by the cdf-2 promoter [Pcdf-2::TTM-1B::GFP] (H) (n = 20).