Table 1. A comparison of the algorithms on simulated mutation data with varying passenger mutation probability 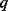 .
.
Avg. distance 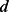 from planted pathways from planted pathways |
|||
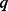
|
Multi-Dendrix | Iter-RME | Iter-Dendrix |
| 0.0 |
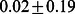
|
0.01
 0.12
0.12
|
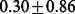
|
| 0.0001 |
0.02
 0.18
0.18
|
0.01
 0.16
0.16
|
0.30
 0.86
0.86
|
| 0.0005 |
0.04
 0.23
0.23
|
0.10 0.40 0.40 |
0.35 0.89 0.89 |
| 0.001 |
0.10
 0.35
0.35
|
0.32
 0.60
0.60
|
0.44
 1.01
1.01
|
| 0.005 |
0.44
 0.71
0.71
|
– | 0.75 1.07 1.07 |
| 0.01 |
1.03
 1.00
1.00
|
– | 1.20 1.15 1.15 |
| 0.015 |
1.68
 1.16
1.16
|
– | 1.78 1.26 1.26 |
| 0.02 |
2.17
 1.24
1.24
|
– | 2.21 1.29 1.29 |
Italicized rows correspond to values of 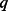 approximated from real cancer datasets. Each entry is mean (
approximated from real cancer datasets. Each entry is mean (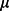 ) and standard deviation (
) and standard deviation ( ) (across 1000 simulations) of the distance
) (across 1000 simulations) of the distance 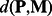 between the planted set of pathways
between the planted set of pathways  and the collections
and the collections 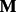 found by each algorithm. The minimum distance
found by each algorithm. The minimum distance 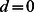 indicates an algorithm found the planted pathways exactly, while the maximum distance
indicates an algorithm found the planted pathways exactly, while the maximum distance 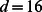 indicates that an algorithm did not find any of the genes in the planted pathways. Bold text indicates the top performing algorithm for each value of
indicates that an algorithm did not find any of the genes in the planted pathways. Bold text indicates the top performing algorithm for each value of 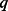 . Multi-Dendrix is the top performer for all values of
. Multi-Dendrix is the top performer for all values of 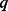 except the smallest
except the smallest 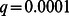 . The differences between Multi-Dendrix and both Iter-Dendrix and Iter-RME are statistically significant (
. The differences between Multi-Dendrix and both Iter-Dendrix and Iter-RME are statistically significant (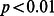 ) for
) for 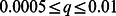 . For
. For 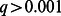 , Iter-RME did not complete after 24 hours of runtime.
, Iter-RME did not complete after 24 hours of runtime.
