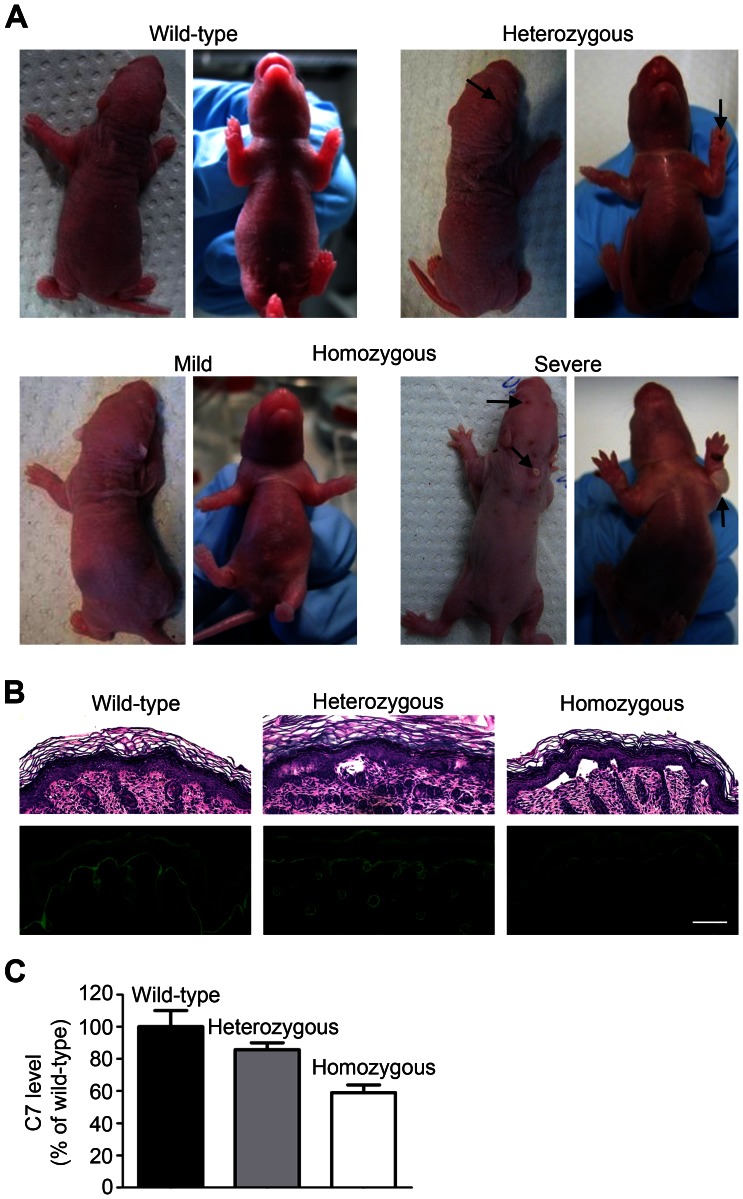
Figure 4. Dominant inheritance and gene-dosage effect of the mutation.
A, Two-day-old rat pups, wild-type, heterozygous or homozygous carriers of the p.G1867D mutation. The heterozygous pups were generated from breeding wild-type males with homozygous females. Heterozygous rats display blistering of paws and back skin (arrows); the phenotype is milder than that of the homozygous pups (gene-dosage effect). B, H&E and immunofluorescence staining of the skin of newborn wild-type, heterozygous or homozygous rats. Note the limited dermal-epidermal separation in heterozygous skin, but extensive separation in homozygous skin. The mutation leads to a reduction in the C7 content at the DEJZ, as seen by C7 immunostaining. The reduction is more pronounced in homozygous animals. Scale bar = 100 µm. C, Semiquantification of C7 staining in B.