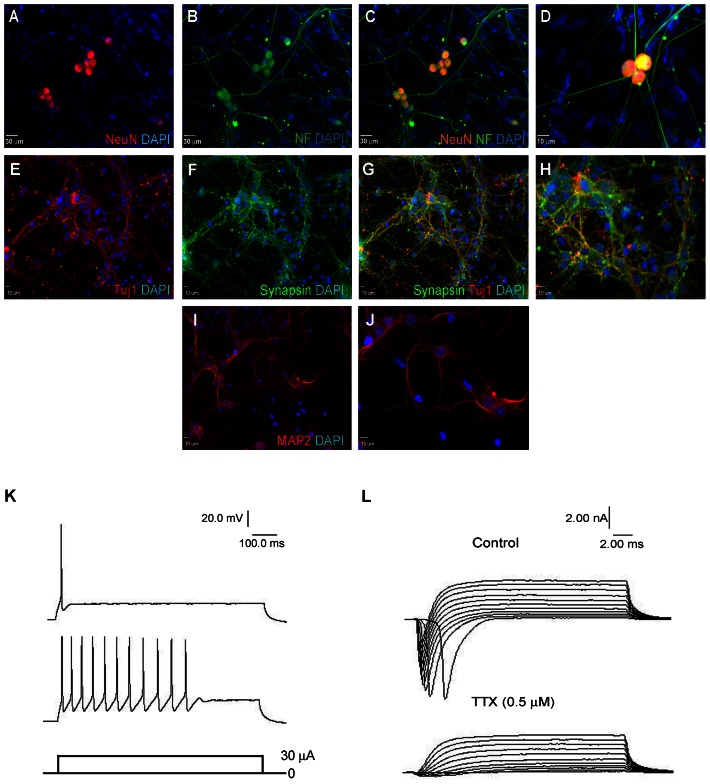
Figure 3. hiPS cell-derived neurons exhibit functional neuronal characteristics.
(A–J) hiPS cells differentiate to mature neurons that express the neuronal markers NeuN (A), Neurofilament L (B), Tuj1 (E), Synapsin1 (F), and MAP2 (I) 4 weeks after terminal differentiation on Matrigel. (C) and (G) are merged images from (A–B) and (E–F), respectively. (D) is a magnified image of hiPS cell-derived neurons. (H) and (J) are magnifications of (G) and (I), respectively. Green is NF-L and synapsin; blue is DAPI; and red is NeuN, Tuj1 and MAP2. Bar = 30 µm for A to C, 10 µm for D–J. Images were chosen from areas dense with cells showing neuronal morphology. (K) Representative action potentials measured from hiPS cell-derived neurons 4 weeks after terminal differentiation. Most cells showed a single action potential spike while some exhibited a train of action potentials. The recorded action potentials are in response to 30 µA current injections under current clamp mode. n = 10 neurons. (L) Top panel shows rapid inward and slow outward currents elicited by step from −40 to 60 mV from a holding potential of −70 mV in hiPS cell-derived neurons 4 weeks after terminal differentiation. The rapid inward sodium current disappears with the addition of 0.5 µM TTX, a sodium channel blocker (lower panel). n = 10 neurons.