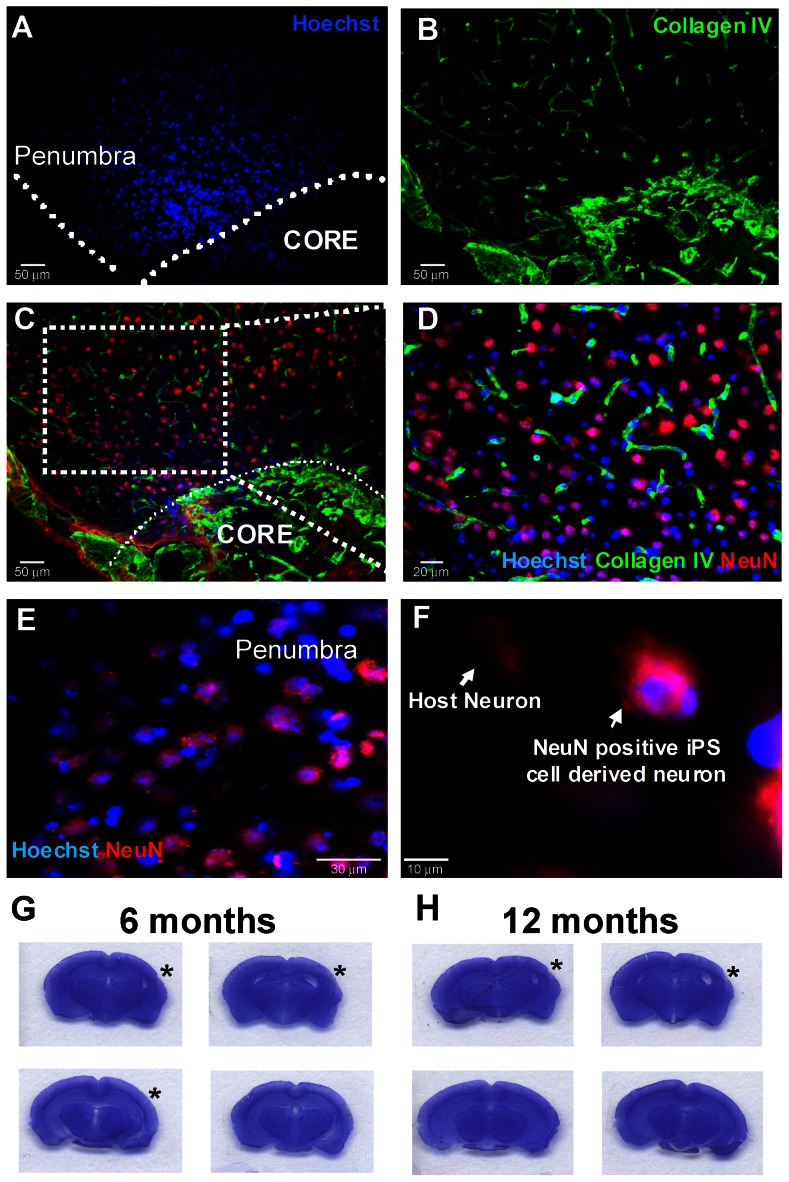
Figure 4. In vivo survival and differentiation of hiPS-NPs in the ischemic brain.
(A–D) hiPS cells survive and differentiate to neurons 28 days after transplantation in the cortex penumbra region of stroke animals. The core region is delineated in (A) with the Hoechst 33342-positive hiPS cell-derived neurons residing in the penumbra. hiPS cell-derived neurons are identified by co-labeling Hoechst-33342 and NeuN. (D) is a magnified image of the marked area in (C). Blue is Hoechst-33342, green is Collagen IV (vessel marker) and red is NeuN. (E, F) are further magnifications to show the co-labeled Hoechst 33342-positive NeuN-positive hiPS cell-derived neurons. A Hoechst 33342-negative NeuN-positive host neuron is also shown in (F). Bar = 50 µm for A to C, 20 µm for D, 30 µm for E and 10 µm for F. (G–H) Nissl staining of brain sections representing brains of hiPS-NP transplanted animals 6 and 12 months after transplantation showing no indication of tumor formation. Asterisks indicate stroke location. N = 6 per group at each time point. (I) The in vivo experimental design for hiPS-NP transplantation and post-stroke experiments.