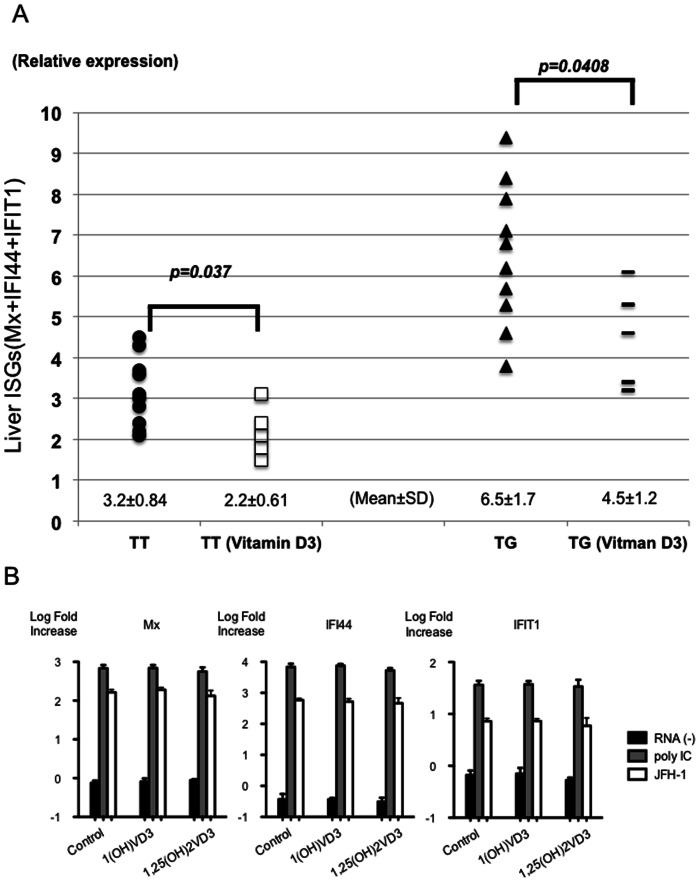
Figure 6. The effect of vitamin D3 on the expression of ISGs mRNA in the liver.
The relative amount of target mRNA was obtained by using a comparative threshold cycle (CT) method. The expression levels of Mx, IFI44 or IFIT1 mRNA in an IL28B T/T patient treated without 1(OH) vitamin D3 are represented as 1.0 and the relative amounts of target mRNA in the other patients were calculated by the comparative Ct method [42]. Therefore, the standard amount of 3 ISGs (Mx, IFI44 and IFIT1) is 3. The relative amounts of the 3 kinds of ISGs were added and shown in the graph (A). Black circles indicate the data from IL28B (T/T) subjects treated without 1(OH) vitamin D3. White boxes indicate the data from IL28B (T/T) subjects treated with 1(OH) vitamin D3. Black triangles indicate the data from IL28B (T/G or G/G) subjects treated without 1(OH) vitamin D3. Black lines indicate the data from the subjects treated with 1(OH) vitamin D3 (A). The effect of vitamin D3 on the expression of ISGs mRNA in the hepatocyte cell culture are shown (B). Huh-7 cells were treated with ethanol (control), 1(OH) vitamin D3 (1.0 µM) or 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 (1.0 µM) after transfection of poly IC (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) or in vitro transcribed JFH-1 full-length RNA. Cells were harvested 30 h after transfection, and the expression levels of Mx, IFI44 and IFIT1 mRNA were assessed by real-time PCR using TaqMan Gene Expression Master Mix (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA) and gene-specific primer and probe sets (TaqMan Gene Expression Assay; Applied Biosystems) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The expression levels of genes with or without vitamin D3 treatment were expressed by log fold increase of untreated Huh-7 cells.