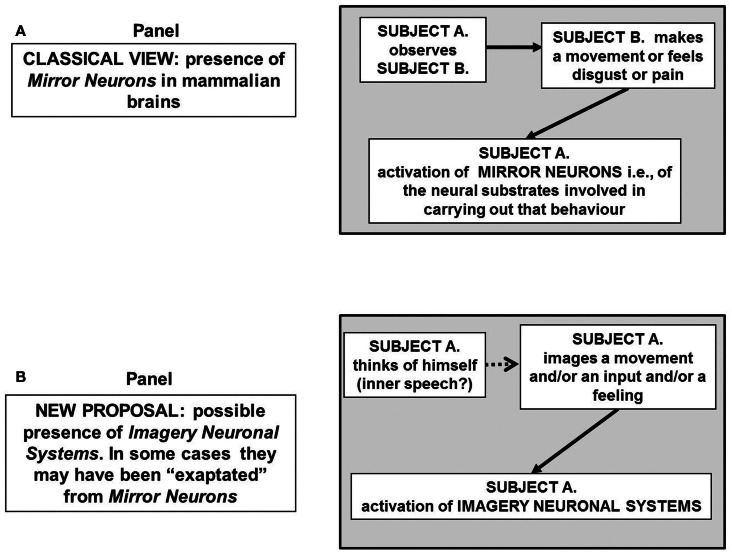
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the possible block diagram representing the functional links leading to the “mirror neurons” that is of neurons that neuron “mirror” the behavior of activated motor neurons even if the observer is not really acting (A) hence mirror neurons sub serve two different functions. In (B) the hypothesis is put forward that some mirror neurons could be part of a broader system, the imagery neuronal system, existing in the human brain, and likely in the brain of at least great apes. The activation of such a system is not necessarily dependent on a sensory input. For further details, see text.