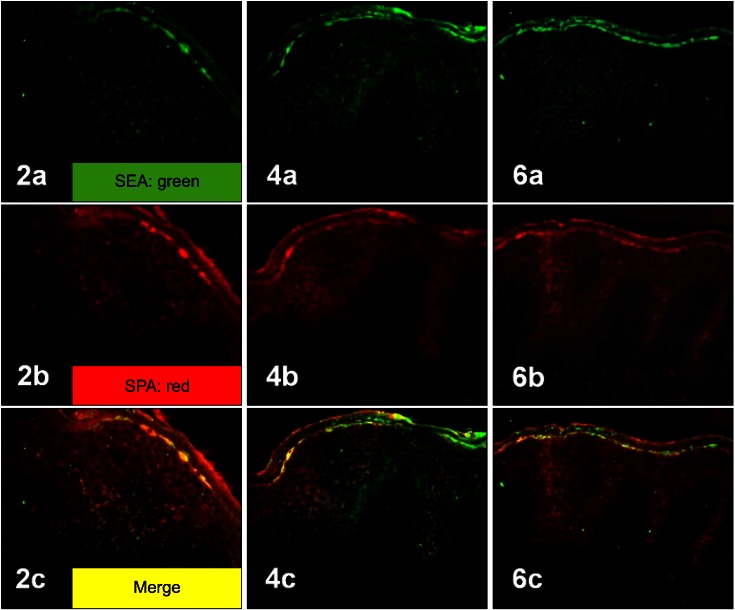
Fig. 2.
Two-colored double-labeled immunofluorescent staining of SEA (a: green), SPA (b: red) and their merged image (c: yellow) in the epidermis of three atopic dermatitis patients (2, 4, 6). Co-localization of SEA and SPA was observed in merged images (yellow), suggesting the coexistence of SEA and Staphylococcus aureus itself in the epidermis of AD patients (2c, 4c, 6c) (2a~6c: ×200). SEA: staphylococcal enterotoxin A, SPA: Staphylococcal protein A, AD: atopic dermatitis.