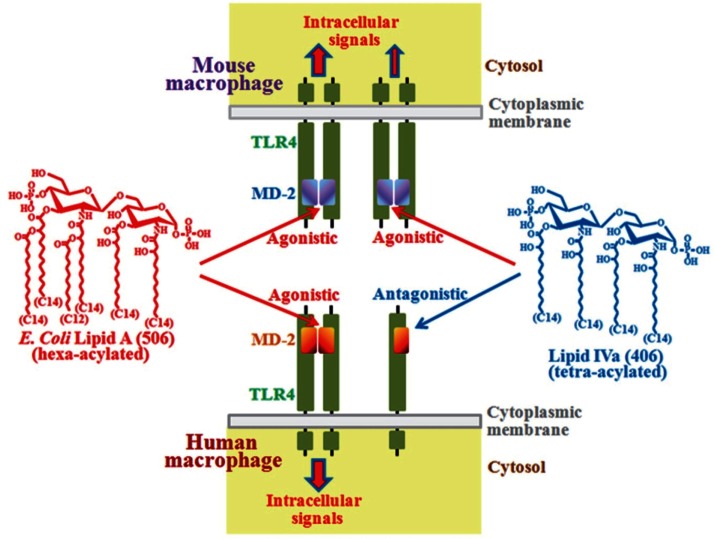
Figure 2.
Differential recognition of lipid A structures between human and mouse TLR4/MD-2 complexes. TLR4 is a type I transmembrane molecule, and MD-2 is an extracellular molecule that associates with the extracellular region of TLR4. Lipid A can bind to MD-2 but not to TLR4. Binding of lipid A to MD-2 induces dimerization of the TLR4/MD-2 complex for transduction of stimulatory signals into cells. Recognition of lipid A structures by mouse MD-2 and human MD-2 is different. For example, E. coli type hexa-acylated lipid A is recognized as a strong agonist by both mouse and human MD-2 that causes dimer formation. On the other hand, tetra-acylated lipid IVa can bind to both types of MD-2, but subsequent dimer formation is achieved only by the mouse system and not by the human system. Once this structure binds to human MD-2, dimer formation is suppressed, and as a result, this structure acts as an antagonist.