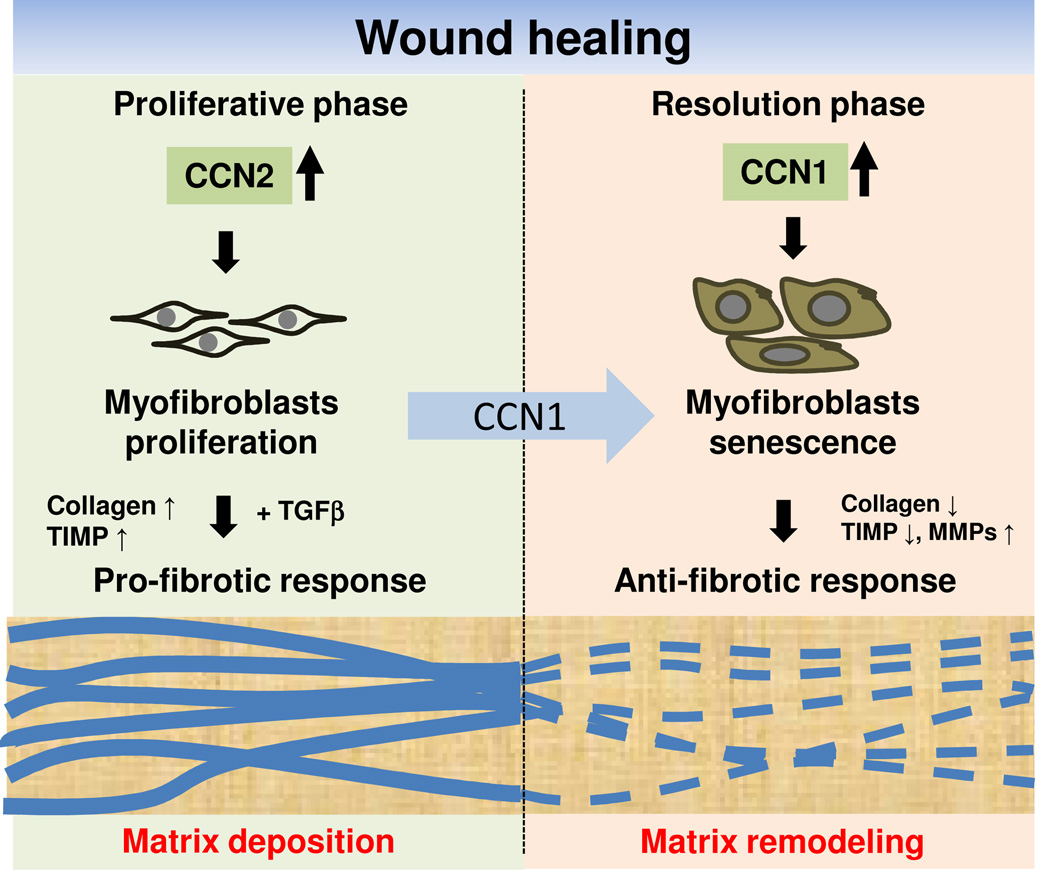
Figure 4. Role of CCNs in wound healing.
CCN1 and CCN2 have distinct roles in wound healing. CCN2 functions in the granulation tissue during the proliferative phase and acts with TGF-β to promote the synthesis ECM, leading to a pro-fibrotic response. As wound healing progresses, CCN1 accumulates to a sufficiently high level to induce an anti-fibrotic senescence switch in myofibroblasts, thereby limiting fibrosis by converting the ECM-synthesizing myofibroblasts into ECM-degrading senescent cells.